VERTEBRAL COLUMN AND THE INTERVERTEBRAL DISC
- Are you living in greater or central London and suffering from back pain?
- Do you have a herniated disc in the lumbar or cervical area?
As a leading back injury London rehabilitation expert and elite personal trainer, you will benefit from my long-term successful professional experience in rehabilitating all types of back disorders.
You may not know but before qualifying in injury rehabilitation, I suffered from very serious back pain.
Learn how Hayley, Jan, Dr Christian, Michaela, Elizabeth Tiffany , M Taylor and Franco successfully rehabbed their back injuries and beat their back pain.
If you are suffering from any type of back injury, apply now here for your FREE CONSULTATIONS.
Back injuries can create long-term consequences such as life lasting neurological damage.
If they are not addressed properly and safe as they should be – the pain and injury could escalate quickly.
Did you know that your vertebral column is one of the most vital structures in your body 2?
It is made up of 33 bones located in different areas of your body:
- 7 cervical (neck),
- 12 thoracic (upper back),
- 5 lumbar (lower back),
- 5 sacral (pelvis bone) and
- Coccyx (tailbone)2.
Your spinal column not only provides stability but also acts as a connection between the upper and the lower extremities 3.
However,
Have you ever thought about what makes the bones in the vertebral column flexible and absorbs all the shocks placed on the back during daily living activities?
Since bones are stiff, right?
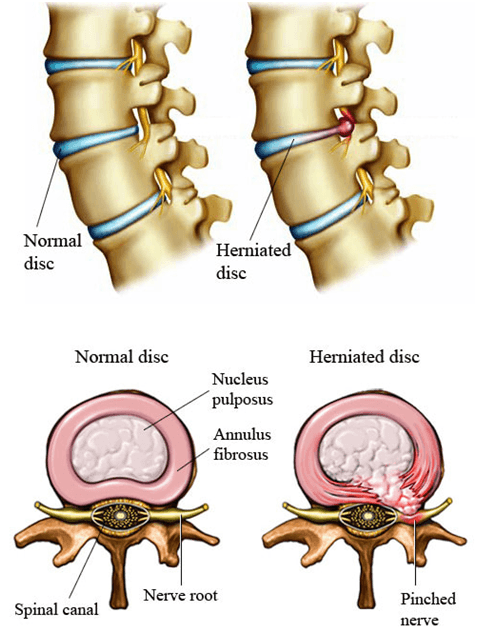
It is the intervertebral discs2!
The disc is present throughout the vertebral column except for the first two cervical vertebra and coccyx5, 3.
WHAT IS AN INTERVERTEBRAL DISC?
Your intervertebral disc is a sponge-like structure that keeps the vertebrae separated from one another and acts as a shock absorber during any type of activity 1, 4.
It is also one of the largest structures of the body but unfortunately, it does not have blood supply 5.
So how does the disc gets its nutrients?
It is through the blood supply of the adjacent structures 4.
In addition, I have a few more questions for you.
- Have you wondered what this disc looks like?
- Did you know that there are 23 discs in the human spine made up of fibrocartilaginous material 3, 4?
Let me clarify these things for you.
The outer part of the disc is the strong annulus fibrosus, and the inner part is a jelly-like called nucleus pulposus 1.
When you perform any type of activity, the inner gel spreads evenly to redistribute the pressure thereby acting as a shock absorber 6.
However, the upper and the lower part of the vertebral body also has a coating, this is called endplate 5.
- Are you suffering from sciatica pain, neck pain, scoliosis, musculoskeletal disorders (MSK) and are looking for someone you can trust?
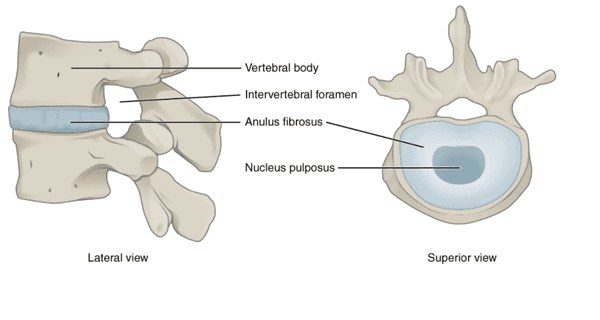 Figure: Intervertebral Disc Structure5
Figure: Intervertebral Disc Structure5
As you age, the intervertebral disc deteriorates with age, which might lead to chronic back pain, especially the lower back 5.
The most common condition leading to back pain is disc degeneration 1.
WHAT CAN CAUSE DEGENERATION OF THE DISCS?
Well,
To begin with – the vertebral disc is a flexible structure 5.
However,
Did you know that the discs could also wear out due to loss of fluid in the disc?
The lower the fluid the less the ability of the disc to absorb shock 7.
Ageing Degeneration
Did you know that ageing is one of the most common factors, which causes the disc to degenerate 4?
As you age, the water and the protein content of the cartilage changes causing them to degenerate 7.
However, this is not all thus; I attach here a few more causes of disc degeneration:
- Repetitive lifting of heavy weights,
- Narrowing of the spinal canal (spinal stenosis),
- Pregnancy,
- Sitting for long hours in front of a computer and poor posture are other common causes of disc degeneration 8, 9, 10.
Herniated disc can lead to a variety of back disorders, which can have an adverse effect on daily living activities.
A few of them are:
- Disc herniation in the cervical area
- Disc herniation in the thoracic area
- Disc herniation in the lower lumbar area
- Sciatica
- Scoliosis
Cervical Disc Herniation
This is a common problem seen in your neck area.
If the degenerated disc compresses any nerve then the pain might radiate in the arm.
Common symptoms of disc herniation in cervical spine include numbness or tingling sensation in the neck and shoulder, which as stated earlier might radiate to the arm.
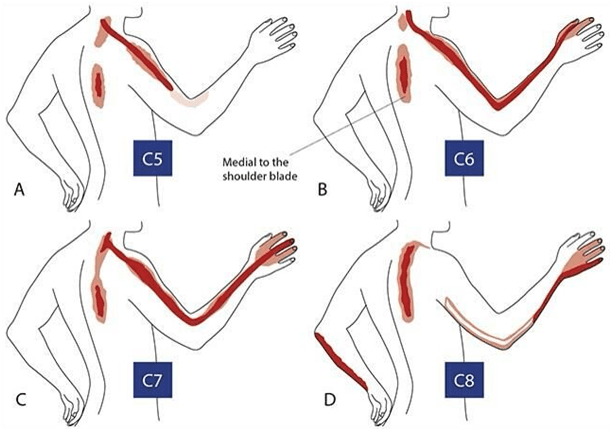
This further leads to a weakness in the arms and hands, and loss of fine motor skills in the arm and hand 11.
Thoracic Disc Herniation
This may lead to pain in the upper back or the mid-back.
If the nerves are compressed the pain radiates to the forearms and the ribs.
You might feel pain in your chest and upper abdomen 12.
Lumbar Disc Herniation
Disc herniation in the lumbar spine or lower back area is very common and may cause a pain in the lower back, which may be either continuous or intermittent.
The pain worsens on coughing, sneezing, if you are working in front of a computer long hours or standing in one position for a long time.
Other symptoms include:
- spasm of the back muscles,
- radiating pain down to the leg and ankle,
- weakness and numbness in the leg muscles and foot,
- change in bladder and bowel function,
- Difficulty in walking 13.
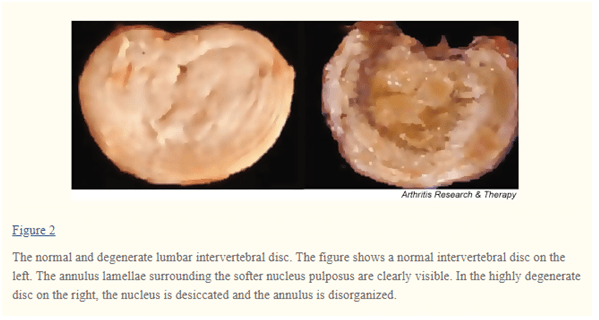
Figure: Disc degeneration 4
Sciatic Nerve
This large nerve running from the lower back to the back of each leg.
Pain due to impingement of the sciatic nerve is sciatica.
Sciatica causes pain in the lower back that may go down to the leg (the side becomes affected).
The pain in the lower back increases during coughing, sneezing, bending or if you are working for long hours in front of a computer.
Apart from the usual causes of disc degeneration- ageing, wear and tear, or hereditary changes other causes of sciatica include:
- Pregnancy
- Spinal Stenosis (Narrowing Of Spinal Canal),
- Piriformis Syndrome,
- Spinal Tumors,
- Infection Or
- Fractures are another common cause of sciatica 14.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis occurs when the spine curves sideways, and looks like alphabet “S”.
The cause of scoliosis is an underlying condition, such as cerebral palsy.
Most of the times it does not have a definite cause.
It is common in children or young adults.
The curved spine puts a pressure on the lungs, thereby affecting the normal breathing pattern.
The most common visual sign of scoliosis is uneven shoulders 22.
Other symptoms include:
- More prominent shoulder blades,
- Ribs on one side may have more gap than the other side, which get clustered together,
- One hip higher than the other 22.
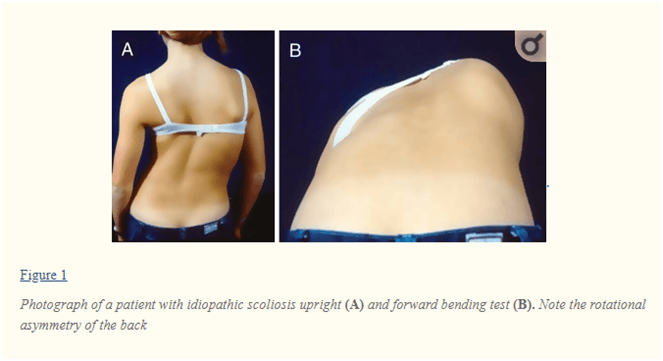
Figure: Scoliosis22
Treatment and Rehabilitation of Disc Herniation
Nowadays there are many types of treatments and back rehabilitation for managing disc herniation.
These methods are mainly in the form of:
- Medicines,
- Physical therapy,
- Occupational therapy,
- Customised exercises and the last resort,
Drug Treatment
What do you do immediately to relieve the back pain?
You take medicines.
Now are you aware, which medicines would actually relieve your pain.
These are Tylenol and NSAIDs like Ibuprofen 15.
Physical Therapy
You can also reduce your pain and other symptoms by the use of electrical modalities.
Electrical mode of treatments mainly include:
- Short wave diathermy,
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (tens), etc.17
The above treatment methods are not the end.
There are varieties of other treatment methods also available.
These are mainly exercises with the aim of maintaining the stability of the lumbar spine and increase your back health.
Pilates
Have you heard of this now-a-days famous form of exercise – Pilates?
It uses very smart functional exercises to increase the flexibility, strength, and range of movement in the joints, balance and posture of an individual 16, 17.
Pilates works using a variety of smart exercise and movements and focused principles.
Your body works with your mind with the aim of maintaining stability of your muscles of the back, abdomen and pelvis; reduce pain; strengthen muscles, increase balance and the range of motion 16, 17.
The Pilates Method of Exercise also improves the flexibility of your spine and muscles if you have chronic lower back pain 21.
Pilates implies the use of a:
- Pilates mat,
- Barrels,
- Wunda chair,
- Reformer or a special piece of equipment called
- Cadillac21.

Figure: The Cadillac 21
You always want to make sure that while performing Pilates your spine is maintained in a neutral stable position whilst you are performing difficult tasks.
Therefore, it is important that you maintain your body weight forward on the balls of your feet 21.
Any movement you find complex, break it down into small patterns.
Irrespective of your age and exercise performance levels, you will hugely benefit from Pilates21.
Yoga
Yoga is a great way of preventing and treating disc degeneration 18.
Various postures in yoga stretch the muscles of the back, thigh and legs.
However,
There are also serious dangers coming from various Yoga exercises.
Some of these yoga asana (poses)are:
- Bharadvajasana, Marichi, or ArdhaMatsyendrasana – seated twisted poses – involving spine rotation on multiple joints
- Padmasana, Bharadvaja or Agnistambhasana asana – Matsyendrasana – these are just a few poses that could injure your knee joint ligament.
I suggest that you always discuss with your therapist the main painful areas and avoid yoga postures that might increase back pain or put you at risk of injury.
When comes to Yoga it’s always best to work 121 with a properly qualified Yoga teacher with additional rehab qualifications in back injury.
When used correctly the Yoga exercises helps to prevent injuries and the advances of degenerative disc diseases 18.
However, there are also serious knee and back injury risks so, you must be aware of these.
Core Strength Training
The training of your core muscles is very important since, they activate and improve the strength and flexibility of the core back muscles.
The regained strength of your core back muscle eventually reduces pain, strengthens the back muscles as a whole and improves your posture 18.
Lumbar strengthening exercises
Strengthening exercises of the lower back aim to improve the strength and endurance of muscles thereby reducing pain and increasing the range of motion 20, 17.
The advantage of these exercises is that they are performed continuously without any breaks thereby increasing muscle contraction 21.
Free Consultation
If you or any of your loved ones are suffering from severe back pain or pain radiating in your hips or legs, then contact me now for your FREE CONSULTATIONS.
I specialise in the area of back pain rehabilitation and spinal conditions.
Hiring a certified personal trainer for relief of symptoms
You always must have a clear goal in mind when you hire an injury rehab expert or an elite personal trainer since they can help you manage and improve your condition.
You will just require clearance to exercise from your MD, physiotherapist, osteopath or health care professional.
Whatever your goal might be:
- Weight loss,
- Reduce pain,
- Gain strength,
- Flexibility
- Range of movements in the joints
- Prevent muscle loss, degeneration or
- Improve posture.
As an elite personal trainer in London specialised in injuries I will help you achieve your health and fitness goals.
You should always hire a personal trainer who can:
- Assess your current fitness level
- Help you find a realistic personal training programme and progress safely with your rehabilitation programme
- Work with you to achieve your goal through the fitness programme level
- Teach you the correct way of exercise
- Minimise and eliminate re-injury risks
- Offer customised support and inspiration
- Provide continuous motivation throughout
- Work with your physiotherapist or your health care provider to professionally discuss your progress and modify your exercise program accordingly
Summary
Disc degeneration is a common condition.
It can occur due to wear and tear of the disc seen during ageing, pregnancy and any other relevant spinal condition or hereditary condition.
The major symptoms include intermittent or continuous pain in the involved region.
If there is any compression of the nearby nerves, the pain can also radiate to the involved upper or lower extremity.
You can manage the condition by a variety of treatment methods that must be customised to your specific needs.
The most important being 121 Pilates exercise, yoga, customised core muscle strengthening and lumbar strengthening exercises.
Tylenol and NSAIDs are other forms of conservative treatment.
Discuss now with Jazz Alessi all your symptoms in details using this FREE CONSULTATIONS.

Once I receive your email,
I will professionally assess your injury history, current state, challenges and goals and provide you with a custom designed back care programme best suitable for your back rehabilitation plan.
References
- Lundon K, Bolton K. Structure and function of the lumbar intervertebral disc in health, ageing and pathologic conditions. Journal of Orthopedic and Sports Physical therapy. 2001;31(6):291-306.jospt.org/doi/pdfplus/10.2519/jospt.2001.31.6.291
- Desai C, Agarwal A. Anatomy, back, vertebral column. Stat Pearl Publishing. 2019.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525969/
- How does spine work? Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care. 2019.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279468/
- Jill PG Urban, Sally Roberts. Degeneration of intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5(3):120-130.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC165040/
- Joshua A, Futterman B. Anatomy. Back, intervertebral disc. Treasure Island (FL). 2018.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470583/
- Chen S, Fu P, Pei M. Meniscus, articular cartilage, and nucleus pulposus: a comparative review of cartilage-like tissue in anatomy, development, and function. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;371(1):53-70.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5645221/
- Low back fact sheet. National Institution of Neurological Disorder and Stroke. 2019;18(15).ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Low-Back-Pain-Fact-Sheet
- Chester J, Donnally III, Varacallo M. Lumbar degenerative disk disease. Treasure Islan (FL). 2019.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448134/
- Katonis P, Kampourogolu A, Aggelpoulos A, et al. Pregnancy-related low back pain. 2011;15(3):205-210.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3306025/
- Billy GG, Lemieux SK, Chow MX. Lumbar disc changes associated with prolonged sitting. PM R. 2014:6(9):790-795.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4152382/
- Yeung JT, Johnson JI, Karim AS. Cervical disc herniation presenting with neck pain and contralateral symptoms: a case report. J Med Cas Rep. 2012;6:122.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3411405/
- Shirzadi A, Drazin D, Jeswani S, et al. Atypical presentation of thoracic disc herniation: case series and review of literature. Case Rep Orthio. 2013.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3638501/
- Amin RM, Andrade NS, Neuman BJ. Lumbar disc herniation. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017;10(4):507-516.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5685963/
- Davis D, Vasudevan A. Sciatica. Treasure Island (FL).2019.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507908/
- Salzberg LD, Manusov EG. Management options for patients with chronic back pain without an etiology. Health Serv Insights. 2013;6:33-38.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4089831/
- Patti A, Bianco A, Paoli A, et al. Effects of Pilates exercise program in people with chronic low back pain. Medicine (Baltimore).2015;94(4):e383.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4602949/
- Bhaduria EA, Gurudut P. Comparative effectiveness of lumbar stabilization, dynamic strengthening, and pilates on chronic low back pain: randomized clinical trial. J ExercRehabil. 2017;13(4):477-485.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5667628/
- Jeng C, Cheng T, Kung C, et al. Yoga and disc degeneration in cervical and lumbar spine: an MR imaging-based case control study. 2011;20(3):408-413.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3048237/
- Akhtar MW, Karimi H, Gilani SA. Effectiveness of core stabilization exercises and routine exercise therapy in management of pain in chronic non-specific low back pain: A randomized controlled clinical trial. 2017;33(4):1002-1006.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5648929/
- Ko K, Ha G, Yook Y, et al. Effects of 12-week lumbar stabilization exercise and sling exercise on lumbosacral region angle, lumbar muscle strength, and pain scale of patients with chronic low back pain. J Phys Ther Sci. 2018;30(1):18-22.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5788767/
- Di Lorenzo, CE. Pilates: What is it? Should it be used in rehabilitation? Sports Health. 2011;3(4):352-361.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3445206/
- Janicki JA, Alman B. Scoliosis: review of diagnosis review and health. PaediatrChild Health. 2007;12(9):771-776.www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2532872/