We are all looking for the magic spring that will restore our physical health, maximise our mental health and make us young and beautiful forever.
And of course, this is nothing to be ashamed of.
However, considering the fact that no one ever found that magical fountain,
We have no other option but to believe it might not really exist.
But, instead, we can make it!
Believe it or not, this magical spring you are waiting to find on the outside can simply flow within you.
By adopting consistent, simple health and beauty routines that will make you look younger and more beautiful.
According to expert women weight loss trainers and rehab specialists:
One effective simple thing to do is: work out.
Working out isn’t all about dropping pounds, getting the body composition in London or prepping for your next London marathon or triathlon.
As an expert women weight loss trainer, I know first-hand that regular exercise could give you a healthy, glowing look and an unmistakable va-va-voom
…which happens to be one of the most-wanted women’s health fitness goals.
I know what you are thinking…
Exercising is:
- Exhausting,
- Slow when it comes to visible results,
- Complicated when speaking of a customised plan,
- Too time-consuming to fit in your busy schedule.
WELL, maybe it is time to change your mind about working out and start your journey towards the most attractive look and the most ideal body composition in London.
In this article I will show you how you can transform your body shape, confidence and worth and maximise your beauty, health and glow.

Not Only Adaptive, But also Addictive!
If you are new to exercising, you definitely look at those who regularly exercise and wonder:
Don’t they feel tired?
Don’t they prefer to spend the day watching the telly and eating cookies instead of sweating at the gym?
Are they always energetic and motivated?
The answer is, when you start exercising, at first it might feel:
- Exhausting
- May be a bit hard
- Some muscle pain
- Not fun
- Not as enjoyable as most of the activities you usually do.
But this is just temporary!
Let me give you an example.
- In a Women’s Health Study, women who walked briskly for just 60-90 minutes per week – cut their risk for cardiovascular, heart attack and stroke by HALF!
The key is exercising consistency.
As you exercise regularly, your body starts adapting to the type of exercise you perform.
- Your muscles get stronger
- Your heart gets more powerful
- Your vessels deliver blood more efficiently
- Your lungs provide more oxygen
- Your muscles get more capable of extracting and utilizing oxygen
- You can breathe deeper and you no longer feel out of breath. [1]
- Boosts your mitochondria (small units inside your cells which are producing more energy).
With all these physiological changes that your body undergoes, exercising becomes an easy thing to do.
On top of that, when exercise is introduced to your system and you cross the adaptation phase, it is very difficult to quit. [2]
In fact, exercising is a very powerful mood-booster.
It is proved that exercising increases serotonin secretion within our bodies. [3]
This is a hormone which is known as the hormone of happiness.
For this reason, exercising regularly will help you continue exercising, stay motivated and reach even the thought-to-be impossible women’s health fitness goals.
All you need to do is START!
Just start safe (be moderate) to avoid injury risks.
Don’t push too hard because exercise addiction is reported as a real problem that must be avoided. [2]

Exercising is not all about losing fats, building muscles, correct posture and getting more shape and definition.
In fact, these benefits help you look more attractive.
But there are countless benefits that go unnoticed because people speak less of it.
Here’s a peek into a few of the ways exercise can make you look and feel fantastic.
- Better Skin
If you think exercising and glowing skin are irrelevant to one another, here are some facts that will make you reconsider.
First of all, exercising improves circulation to your body cells.
This means more nutrients and oxygen are delivered to every cell in your body parts – including your skin –
It also stimulates your cells to secrete specific substances such as interleukin-15, a protein that boosts your metabolism, stimulates cell regeneration and increases the life span of your cells. [4]
As a result, cells can function and regenerate efficiently making you look younger and brighter.
In other words, exercising gives you:
- Elastic skin
- Vibrancy and brightness
- Less acne and skin breakdowns
- Well-hydrated skin
- Less cellulite and sagging
- Less wrinkles as you age [4]
Would you like to find out the best form of exercises that will help you improve your skin condition?
Receive free professional advice from Jazz Alessi, our elite women weight loss trainer.
Request a FREE CONSULTATION now!
- Attractive Posture
Having postural abnormalities reduces your attractiveness.
For example, if you have a slouched back, your belly appears larger as it pops out.
Exercising, on the other hand, tightens you up and gives you the model-like posture and the springy steps that will make you look and feel more attractive. [6]
- Chemicals – Toxins – Free
Exercising means sweating.
And although no one likes to be sweaty, sweating is a physiological process that helps your body get rid of toxins through the skin.
Sweating purifies your skin pores and helps your body become fresh from inside out.
All you need to do is take care of your personal hygiene and shower directly after exercising to gain the best benefits. [5]
From now on, SAY YES TO SWEATING!
In addition to all the benefits I have just mentioned, there are other benefits too.
In general, exercising gives you:
- Smoother, more radiant skin
- Greater self-confidence
- Increased stature
- Less Stress and Anxiety
- Better Immunity and Detoxification
- More Restful Sleep
- Less Visceral Fat
- Stronger Sex Hormones
- Improved mood and psychology
- Better posture
- Less ageing signs (e.g. wrinkles) [1]

Bad and Good Pain: Which is Which?
If you are a beginner, you might have heard of muscle soreness and pain associated with exercising.
You might have also heard these types of pain are normal after a hard workout.
This is why you probably tend to bear any kind of pain that may appear as you exercise.
Yet, not all pains are the same.
It is important to listen to your body and try to differentiate between different types of the pain you feel.
This is crucial because not every pain is normal.
Some types of pain, when felt, are a red flag for you to stop this exercise move and maybe find an alternative.
Usually, pain originates from:
- Muscles
- Bones
- Tendons
- Ligaments
- Nerves / innervations
Good Pain
Usually, soreness occurs in the 24-48 hours following the exercise. (Hence the name delayed onset muscle soreness – DOMS).
This type of pain is caused by stimulation of the chemical nociceptors (pain receptors) within the muscle in response to the increased production of waste products (e.g. lactic acid) [1]
This type of pain is normal and can be relieved by:
- Rest
- Hot showers
- Physiotherapy
- Relaxation and meditation
- Proper hydration
- Proper training plan [8]
But you can also relieve DOMS using massage, cold showers or cryotherapy.
The possibilities to reduce muscle discomfort and end pain after exercise are literally endless so, you shouldn’t be afraid of this.
Bad Pain
Bad pain is usually inflammatory in origin.
It originates from already present inflammatory problems that worsen by:
- Repetitive movement (e.g. tennis elbow, frozen shoulder, carpel tunnel syndrome)
- Weight bearing (e.g. arthritis)
- Muscle use (e.g. tendonitis)
Wondering what kind of pain is the pain you feel during exercise? Let me know how this pain feels like and I will guide you through dealing with it. Request a free consultation now!
Exercise as a pain killer
If you complain of hip, knee, ankle, back or shoulder pain, try custom exercise – the tailored to your needs exercise programmes will help you alleviate your pain and enjoy a pain-free life.
This is the case when the pain you are complaining of is caused by:
- Hyper laxity in your ligaments
When your ligaments are lax, your joints are hypermobile.
In this case, when you move, your joints go beyond the normal range and place your tissues in an overstretched position.
This over stretch can cause pain and injuries (e.g. dislocation). [9]
This is why strengthening your muscles can help you stabilise your joints and avoid this overstretch.
- Postural misalignment
Our bones are designed to articulate forming joints and to move smoothly over one another.
If you sit or assume faulty postures for a long time, your bones get misaligned.
This misalignment places abnormal load on your joints and amongst other things it can result in pain and arthritis. [12]
Customised Pilates exercises will strengthen your muscles – especially antigravity muscles that help maintaining your posture – can help you reduce or prevent posture related pain. [11]
- Muscle weakness and imbalance
Lack of physical activity leads to muscle weakness and shortening.
The muscles you use very often tighten up and become short.
While the muscles you do not use become weak.
This muscle imbalance leads to:
- Muscle pain with exertion or at rest
- Loss of flexibility
- Loss of endurance
- Abnormal bone alignment and
- Joint pain and arthritis
- Low back pain [13]
Exercising can help you strengthen your weak muscles and stretch your short ones.
Thus, can help you get rid of the pain.
- Natural Pain Killers
It has been proved that exercising of all types and intensities (in different percentages) stimulate the secretion of natural pain killers called endorphins and encephalins.
So, no matter what the type of your pain is, exercising can always make you feel better. [7]

Here are some of the best exercises to get rid of your knee and hip pain once and forever:
- Knee lift
Stand up straight, tuck your abdomen in and raise your leg off the floor with the knee bent.
Repeat for 10-15 times.
EXPERT TIP:
If you have poor balance and have difficulty standing on one leg, you can perform the seated knee lift sitting on a chair.
Sit on a chair nice and tall with your feet on the floor, lift up one leg keeping your knee bent.
Raise it until the back of your thigh is slightly off the chair.
Lower it back to the floor and repeat on the other side.
This exercise will help you strengthen the quadriceps and hamstrings.
- External hip rotation
Strengthening external hip rotators (i.e the piriformis, superior and inferior gemelli and obturator internus) is important because it helps improving stability and preventing injuries in the hips, knees, and ankles.
Strong hip external rotators can also reduce knee and low back pain.
Here are several exercises to strengthen these muscles:
- Clamshell exercise
- Fire hydrant exercise
- Seated figure 4
- Double hip rotation
This exercise stretches and strengthens your hip muscles at the same time.
To perform this exercise, lie on your back with your arms stretched out.
Bend your both knees and place your feet flat on the floor.
Rotate your knees left, the closest you can to floor, hold for several seconds and feel the tension in your muscles as they get stretched.
Repeat on the other side.
EXPERT TIP:
Don’t allow your shoulders to lift off the floor.
- Hip and lower back stretch
Simply lie down and bring your knees to your chest and hold them tight.
This position relieves the tension in your back and hips and helps you assume a better posture.
It can also decrease or prevent low back pain. [14]
- Hip flexion
To work out your hip flexors, stand up nice and tall and place one foot on a chair with your knee bent.
Raise your leg up by initiating the movement at your hip until your foot completely clears off the chair.
Repeat for several times before switching to the other side.
- Hip extension
To train your hip extensors, you can do the bridging exercise like the Pilates shoulder bridge.
Lie down on your back, flex your knees and place your feet flat on the floor for stability.
Tuck your tummy in and raise your hips up away from the floor until your trunk is straight. [14]
Repeat for several times.
This exercise also strengthens your back muscles.
EXPERT TIP:
People who experience hip pain or discomfort for more than an hour following these exercises should reduce the number of repetitions accordingly.

Suffering from Knee pains, meniscus, ACL and PCL injury?
Ligaments are important structures that play a role in stabilising your joints.
At the same time, they are prone to injury due to:
- Hyper laxity
- Awkward posture
- Sudden, vigorous movements beyond normal range
Ligamentous injury is very common in the knee. [15]
This is because the knee is:
- A shallow joint.
- A weight bearing joint.
- Easily affected in contact activities. [16]
We have the meniscus and four ligaments in the knee that are prone to injury:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is the most commonly injured knee ligament. It connects the thigh bone to the shin bone and it accounts for 85% of the knee stability. [16]
- Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) also links the thigh bone to the shin bone in the knee. (It’s rarely injured except in car accidents).
- Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) connects the thigh bone to the fibula, the smaller bone of the lower leg on the outer side of the knee.
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL) links the thigh bone to the shin bone on the inside of the knee
How can a customised exercise plan help?
Many people think that working, moving and exercising is the main reason why injury takes place.
Customise exercise, however, is a very important factor in both preventing and treating injuries.
For instance, strengthening, balance and proprioceptive training make muscles around the knee stronger and more capable of stabilising the joint.
As a result, ligaments are enhanced by muscles and are less prone to injury. [17]
In addition, customise exercise can be the answer to knee pain.
For example, if you are suffering from pain due to patellar mal-tracking (a condition in which the knee cap does not lie in its groove leading to inflammation and pain).
A laser sharp, customised to your condition and goals plan of stretching, strengthening and balance training can solve the problem and help vanish your knee pain.
Say Good-bye to back pain
You feel it each time you bend over or stand up.
It’s that groan-inspiring ache that shoots through your lower back and never seems to fully go away.
Wondering what the reason is?
Well, causes for back pain are countless, it may be originating from:
- Muscles (e.g. muscle strain or spasm)
- Bones (e.g. Spondylosis)
- Ligaments (e.g. sprain or tear)
- Nerves (e.g. nerve compression or entrapment)
In order to get rid of your back pain, you need an assessment based customised exercise plan that targets the cause of pain.
For example, if your pain originates from a faulty posture in your back, an increased or a decreased spinal curve, stretching and strengthening can help you correct your posture and get rid of your pain. [13]
Likewise, if your back pain is neural in origin, a customised plan including nerve flossing exercises can get you rid of these pins and needles forever.

Here are some expert tips on how to relieve your back pain using different forms of exercise
- Try Partial Crunches
You must have tried to do crunches in order to strengthen your abdominal muscles.
You might also have realised how painful they are!
In fact, crunch is not an exercise for everyone.
If your abs are weak, forcing yourself to do crunches places overload on your spine and may provoke or worsen your back pain.
Instead, try another form of abdominal exercises that is more suitable for beginners.
You can try partial crunches, cat position exercises or planks that place less load on your back.
- Skip the Sit-Ups
Like crunches, sit-ups require strong deep core muscles to be performed correctly.
If you are new to exercising, there are more benefits in not doing sit-ups; especially if you already have back pain.
Because core strengthening is crucial, replace sit-ups with planks.
- Hip flexors Stretches
When your hip flexors are tight, they pull your pelvis forward and downward increasing the curve in your lumbar spine.
As a result, the weight of your upper body creates overload on your spine leading to low back pain.
Stretching hip flexors helps you avoid hyperlordosis (exaggerated lumbar curve) and helps decrease and prevent low back pain. [14]
Fight back pain, anywhere, anytime!
With today’s technology, you don’t need to go the extra mile to fit your rehabilitation sessions in your schedule.
Instead, you can meet with your personal trainer online in one-to-one training sessions and gain the benefits of rehabilitation.
Some benefits are to:
- Improve flexibility
- Strength, endurance and fitness, all of which help in the prevention and treatment of back pain
- Improve posture
- Improve mood and mental well-being
- Improve your earning as with this type of customised support your back-pain problem rehabilitates safely and you can do any job you would like to do
- Reduce the risk for other health problems, such as heart problems, diabetes or obesity. [18]

Neck Exercises: Your Way to a Pain-free Neck
You may think of your neck as a safe joint.
You usually don’t expect it to hurt because it is not a weight bearing joint like your knee.
And because it doesn’t allow for a huge range of movement as your shoulder or hip.
Bad news is, your neck is not an exception.
In fact, the neck faces too many challenges including:
- Supporting the weight of the head
- Allowing for flexion and extension
- Allowing for side bending and rotation
- Maintaining erect posture
With all these challenges, the neck’s bones and soft tissues may experience different injuries.
For example, the vertebrae may get inflamed and cause Spondylosis.
Muscles may get weak, switched off, spasmed or strained, and so on…
In almost all cases of neck pain, neck exercises are a common part the treatment plan.
A customised neck exercise programme might consist of a combination of stretching and strengthening exercises and aerobic conditioning. [14]
Just remember, cervical and neck pain rehabilitation is a precise assessment based journey.
- Neck stretches
Get rid of stiff neck and keep your neck moving by regularly stretching your neck muscles and making sure your neck range of movement is full.
In order to do so, make sure you cautiously move your neck through:
- Full extension (backward bending)
- Full flexion (forward bending)
- Full lateral neck flexion (bending side to side)
- Full rotation (turning side to side) [14]
- Neck strengthening
Weak neck muscles can lead to pain, spasm and more serious health problems like disc bulge and Spondylosis.
It is important to strengthen your neck muscles by simply performing the four neck movements against resistance.
You can use your hand to resist movement throughout the range of movement.
Don’t forget to repeat for several times.
- Isometric exercises
If you have neck pain, Spondylosis or acute disc bulge with radiculopathy (nerve pain going down your arm).
It is advised to avoid unnecessary movements in your neck, especially those that provoke your pain.
However, to avoid muscle wasting, you still need to activate your muscles in a safe way.
This is when isometric training can help the best.
Simply resist neck movements using your hand and apply too much resistance that actually prevents your neck from moving.
Isometric exercises are important because they:
- Activate your muscles
- Protect your joints
- Prevent muscle loss
- Do not aggravate your pain [14]
- Aerobic conditioning
Aerobic or “cardio” training is one form of exercise that will help slacken your muscles and increase their endurance.
This means it helps your muscles accommodate to long-lasting activities.
For example, if you walk for 30 minutes every day, your back muscles will be capable of spending more time in a standing position without getting fatigued.
As a result, they will keep supporting your joints as you stand and won’t place extra load on your spine.
- Postural correction
Poor posture with your head too far headfirst may lead to not only neck pain, but also upper back pain, shoulder blade pain, and headaches.
Fortunately, you can correct your head posture using simple exercises like tucking your chin in. This will help you avoid the complications of an awkward posture. [6]
It will also help you stand tall, and look more attractive.
- Customised Pilates Exercises – One on One
If you have neck pain due to desk work, sudden movements, injuries, overuse of your cell phone or poor posture,
And if you are already a fan of open-air training, grab your mat and get ready for Pilates to get rid of your neck pain.
If you are new to Pilates Method Of Exercise, you need to know that Pilates is a whole-body exercise and one of the smartest training methods on earth.
It involves a series of coordinated movements that concentrate on improving:
- Core stability,
- Muscle performance,
- Posture,
- Balance
- Flexibility and
- Your neurology.
In a recent study, Pilates training has been proved effective in treating chronic neck pain in no time. [24],[25]
Surprisingly, it has been proved that when customised Pilates exercises was added to conventional rehab programmes, rehabilitation time was shorter and the improvement was more significant. [26]
In general, Pilates exercise training is unique because it:
- Can be performed anywhere
- Suitable for people with low physical fitness
- Requires minimum or no equipment
- Causes minimal or no soreness
According to research, Pilates exercises are effective in:
- Reducing pain
- Improving both structural and your body functions
- Improving your flexibility
- Improving quality of life
- Reducing the use of pain killers. [24],[25]
- Yoga
Yoga is also effective in:
- Stretching your muscles
- Improving your posture
- Relaxing your body and getting rid of stress
- Reducing muscle spasm
- Reducing stress [19]
When the training is customised all these Pilates and Yoga benefits can help you say goodbye to your neck problems forever.
- Are you concerned about a specific complaint?
- Do you have a vague neck pain?
- Do you want to know if exercising can help you get rid of these?
If your answer is yes contact now Jazz Alessi, the best elite personal trainer in London.
Request a FREE CONSULTATION NOW!

Sitting for too long? Postural correction is a must
Having a good posture is about more than looking attractive. It helps you:
- Improve your strength
- Improve your flexibility
- Improve your balance
- Avoid risks of injuries.
Maintaining a correct posture can lead to less muscle pain and reduce your risk of injury. [6],[12]
We’ve all seen the research about the negative impact sitting for extended periods of time has on our health.
But most of us have to sit, at least for a portion of our day.
This is why we need to address the postural challenges of sitting for long time. These can be:
- Shortening of muscles (e.g. calves and hip flexors)
- Weakness of muscles (e.g. abs, hip extensors and shoulders)
- Muscle strain or spasm
- Abnormal weight bearing on joints (e.g. spine)
- Decreased physical fitness. [20]

Ways to Improve Posture and Alignment:
Sometimes, sitting for long is unavoidable.
Good news is: its complications are preventable.
A very simple thing to do is to reverse the effects of sitting for a long time by:
- Habit modification
Instead of sitting all day, try periodically moving around your desk or standing while having your lunch.
You can also organise breaks all over the day so that you get to walk around and get your body moving.
If your chair is ergonomically inappropriate, change it to a better one. [21]
- Exercise during work
If you have no time for breaks, dedicate minutes to stretch your neck, arms, back and legs while sitting on your desk.
And believe me; these minutes will pay-off when they become a daily habit.
- Dedicate some time for Pilates
If you are looking for the gentle – but effective – training that can:
- Improve your posture and align your spine
- Create a positive body-mind connection
- Improve your flexibility and balance
- Tighten up your body and improve your shape
- Improve your self-esteem and confidence
Pilates is the answer to all your needs. [11],[24]
- Dedicate some time for yoga
Yoga is an ancient System of poses designed to align your body parts together by combining stretching and range of motion exercises in addition to relaxation and coordinated breathing that help you get rid of the stress and tightness in your muscles and stretch more efficiently. [19]
It is also safe if you have previous injuries in your back, hip, or knees because it can be performed with minimal weight bearing on injury sites.
So, with the help of an ACL and PCL injury Trainer in London, You can add some yoga options to your exercise routine safely.
- Pay a visit to your chiropractor
Having a cracky spinal alignment by a chiropractor after a long week of extended sitting and tons of desk work feels like a big relief.
It helps you restore the position of your joints, achieve better results when you exercise and reduce your Lower back pain rehabilitation time.
- Massage Therapy:
When your muscles take your bones out of alignment, you need to restore muscle flexibility in order to get your bones back in order.
After an exhausting day at work, a deep massage can help you slacken your muscles and get rid of all the stress and pain.
- Pilates and core strengthening:
Core Strengthening is the very first step in correcting posture.
Core muscles are deep muscles that act as a corset for supporting and holding your trunk together.
They are more stabilisers than movers.
In addition, they are called postural muscles because they are responsible for maintaining good posture.
So, if you are aiming for improving your posture, core strengthening is where to start. [22]

What is PCOS?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition that affects how a woman’s ovaries work.
Ovaries are the reproductive organs that produce estrogen and progesterone — hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle.
Normally, the ovaries also produce a small amount of male hormones called androgens.
When you have PCOS, these hormones get out of balance.
In other words, your body tends to produce abnormally higher levels of androgen.
This hormonal imbalance affects several aspects of your health and may lead to:
- Infertility
- Metabolic syndrome
- Insulin resistance
- Diabetes risks
- Weight gain
- Sleep apnea
- Eating disorders due to weight gain
- Endometrial cancer
- Depression
- Acne
- Hairsutism (abnormal hair growth with male distribution)
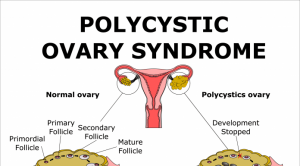
The cause of PCOS is unknown.
However, it has long been connected to insulin resistance.
Good news is: it is proved that following a customised women diet plan in London can help you:
- Boost fat metabolism
- Reduce insulin resistance
- Reduce belly fat that is associated with insulin resistance
- Improve body composition
- Reduce cholesterol levels [23]
Also, in a recent study of exercise training on PCOS, 50% of women diagnosed with PCOS have shown significant improvement in:
- Irregularity of menstrual cycles
- Ovulation
- Body composition
- Insulin resistance
- Androgen production
- Lipid profile [23]
It was also evident that the preferred form of exercising is a cardio workout of moderate intensity or high intensity interval training.
However, both extra weight and high intensity training also present you with an increase in risk of injuries.
Therefore, if you’d like to avoid injuries risks train under supervision.
With the help of a personal fitness trainer London, a combination of a customised nutrition diet plan and exercising can help you improve your symptoms and reduce the negative effect of PCOS on your health. [23]
Do you need a detailed exercise prescription to reduce your PCOS symptoms?
Feel free to speak to Jazz Alessi, our elite Personal fitness trainer London.
REQUEST A FREE CONSULTATION NOW!

Conclusion:
Looking young and feeling healthy and energetic are a challenge for every woman.
With tons and tons of health challenges that women face every day, it sometimes seems like an impossible mission to accomplish.
The good thing is, you can think of exercising as a magic stick.
Together with a customised women diet plan in London, exercising could be a solution to almost every problem you have.
Sweat your pains away
It is definite that no one likes to live with pain. It literally ruins every beautiful moment we are trying to enjoy.
If you have chronic pain in your back, shoulder or neck pain, believe it or not, a customised Lower back pain rehabilitation programme can help you get rid of all those.
Also, if you are suffering from hip, knee or ankle pain due to arthritis or ligament injury, you can use the help of an expert ACL and PCL injury Trainer in London
So that you can enjoy moments with your beloved ones and live the life to its max.
All you need to do is have an exercise plan tailored to suit your health problem.
An expert personal trainer can do that for you.
You just need to stay motivated, follow the instructions carefully and feel proud of yourself as you see the results.
If you have any questions or concerns about the knees, shoulder and advanced back pain rehabilitation, please contact Jazz Alessi on t: 020 3633 2299 (Monday – Fri: 6:30am to 9pm – Saturday: 8am to 3pm).
Request for free consultation here https://www.personaltrainingmaster.co.uk/contactme
For more information regarding services offered at our website, please visit https://www.personaltrainingmaster.co.uk
References
- Rb, Armstrong, W. Gl, Warren Ja, Farrell Pa, Wilmore Jh, Coyle Ef, et al. Chapter 3 – “PHYSIOLOGIC RESPONSES AND LONG-TERM ADAPTATIONS TO EXERCISE.” . https://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/sgR/pdf/chAp3.pdf
- Szabo, Attila & Griffiths, Mark & Kurimay, Tamás & Kun, Bernadette & Urbán, Róbert & Demetrovics, Zsolt. (2012). Exercise Addiction: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Epidemiology, and Etiology. Substance use & misuse. 47. 403-17. 10.3109/10826084.2011.639120. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51979945_Exercise_Addiction_Symptoms_Diagnosis_Epidemiology_and_Etiology
- Meeusen, Romain & Meirleir, Kenny. (1995). Exercise and Brain Neurotransmission. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.). 20. 160-88. 10.2165/00007256-199520030-00004. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/14629527_Exercise_and_Brain_Neurotransmission
- Crane, J. D., MacNeil, L. G., Lally, J. S., Ford, R. J., Bujak, A. L., Brar, I. K., Kemp, B. E., Raha, S., Steinberg, G. R., & Tarnopolsky, M. A. (2015). Exercise-stimulated interleukin-15 is controlled by AMPK and regulates skin metabolism and aging. Aging cell, 14(4), 625–634. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12341 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4531076/
- Eda, N., Shimizu, K., Suzuki, S., Lee, E., & Akama, T. (2013). Effects of High-Intensity Endurance Exercise on Epidermal Barriers against Microbial Invasion. Journal of sports science & medicine, 12(1), 44–51. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3761748/
- Kim, DeokJu & Cho, MiLim & Park, YunHee & Yang, YeongAe. (2015). Effect of an exercise program for posture correction on musculoskeletal pain. Journal of physical therapy science. 27. 1791-4. 10.1589/jpts.27.1791. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280119723_Effect_of_an_exercise_program_for_posture_correction_on_musculoskeletal_pain
- Carolina Ortigosa Cunha, Lívia Maria Sales Pinto-Fiamengui (2016) Is aerobic exercise useful to manage chronic pain? Rev Dor. São Paulo, 2016 jan-mar;17(1):61-4: https://www.scielo.br/pdf/rdor/v17n1/1806-0013-rdor-17-01-0061.pdf
- Zubia Veqar (2013): Causes and Management of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness: A Review Elixir Human Physio. 55 (2013) 13205-13211 https://www.elixirpublishers.com/articles/1361949146_55%20(2013)%2013205-13211.pdf
- Grahame, Rodney. (2009). Joint hypermobility syndrome pain. Current pain and headache reports. 13. 427-33. 10.1007/s11916-009-0070-5. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/38067027_Joint_hypermobility_syndrome_pain
- Candotti, Cláudia & Noll, Matias & Bárbara, & Marchetti, Vendramini & Rosa, Bruna & Da, Maria & Schultz, Graça & Vieira, Adriane & Loss, Jefferson. (2015). Prevalence of back pain, functional disability, and spinal postural changes. Fisioterapia em Movimento. 28. 711. 10.1590/0103-5150.028.004.AO08. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287319097_Prevalence_of_back_pain_functional_disability_and_spinal_postural_changes
- Krawczky, Bruna & Mainenti, Míriam & Pacheco, Antonio. (2016). The impact of pilates exercises on the postural alignment of healthy adults. Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte. 22. 485-490. 10.1590/1517-869220162206153957. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312061661_The_impact_of_pilates_exercises_on_the_postural_alignment_of_healthy_adults
- A. BURT, M.B., B.Chir., M.R.C.P. 1994 Effects of Faulty Posture Jr Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine . vol187 https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/003591575004300315
- Cassio Victora Ruas, and Adriane Vieira 2017 Do Muscle Strength Imbalances and Low Flexibility Levels Lead to Low Back Pain? A Brief Review https://www.sjosm.org/article.asp?issn=1319-6308%3Byear%3D2017%3Bvolume%3D17%3Bissue%3D3%3Bspage%3D123%3Bepage%3D128%3Baulast%3DShetty#:~:text=Exercise%20training%20has%20shown%20significant,in%20turn%20reducing%20androgen%20production.
- Kisner, Carolyn., and Lynn Allen Colby. Therapeutic Exercise: Foundations and Techniques. 5th ed. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis, 2007.
- Hauser, Ross & Dolan, E & Phillips, H & Newlin, A & Moore, R & Woldin, Barbara. (2013). Ligament Injury and Healing: A Review of Current Clinical Diagnostics and Therapeutics. The Open Rehabilitation Journal. 6. 10.2174/1874943701306010001. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236234483_Ligament_Injury_and_Healing_A_Review_of_Current_Clinical_Diagnostics_and_Therapeutics
- Abulhasan, Jawad & Grey, Michael. (2017). Anatomy and Physiology of Knee Stability. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2. 34. 10.3390/jfmk2040034. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320042123_Anatomy_and_Physiology_of_Knee_Stability
- DARIN A. PADUA, PhD, ATC, and STEPHEN W. MARSHALL, PhD University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill : Evidence Supporting ACL-Injury-Prevention Exercise Programs: A Review of the Literature http://exss.unc.edu/files/2013/01/padua_2006_att.pdf
- Abou Elmagd, Mohammed. (2016). Benefits, need and importance of daily exercise. International Journal of Physical Education, Sports and Health. 22. 22-27. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306118434_Benefits_need_and_importance_of_daily_exercise
- Büssing, Arndt & Michalsen, Andreas & Khalsa, Sat Bir & Telles, Shirley & Sherman, Karen. (2012). Effects of Yoga on Mental and Physical Health: A Short Summary of Reviews. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM. 2012. 165410. 10.1155/2012/165410. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231176721_Effects_of_Yoga_on_Mental_and_Physical_Health_A_Short_Summary_of_Reviews
- Daneshmandi, Hadi & Choobineh, Alireza & Ghaem, Haleh & Karimi, Mehran. (2017). Adverse Effects of Prolonged Sitting Behavior on the General Health of Office Workers. Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. 7. 69-75. 10.15280/jlm.2017.7.2.69. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320038864_Adverse_Effects_of_Prolonged_Sitting_Behavior_on_the_General_Health_of_Office_Workers
- American Physical Therapy Association: Posture (PDF) https://fliphtml5.com/zlwu/twsz/basic
- Szczygieł, Elżbieta & Blaut, Jędrzej & Zielonka-Pycka, Katarzyna & Tomaszewski, Krzysztof & Golec, Joanna & Czechowska, Dorota & Masłoń, Agata & Golec, Edward. (2017). The Impact of Deep Muscle Training on the Quality of Posture and Breathing. Journal of motor behavior. 50. 1-9. 10.1080/00222895.2017.1327413. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319181007_The_Impact_of_Deep_Muscle_Training_on_the_Quality_of_Posture_and_Breathing
- Hazarika, Lima & Saikia, Swaraj & Sen, Supriyo & Phukan, Pranay. (2020). Impact Assessment of Nutrition and Physical Exercise on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A Review. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343685487_Impact_Assessment_of_Nutrition_and_Physical_Exercise_on_Polycystic_Ovary_Syndrome_PCOS_A_Review
- Cemin, Natália & Schmit, Emanuelle & Candotti, Cláudia. (2017). Effects of the Pilates method on neck pain: a systematic review. Fisioterapia em Movimento. 30. 363-71. 10.1590/1980-5918.030.S01.AR05. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321463347_Effects_of_the_Pilates_method_on_neck_pain_a_systematic_review
- Ulug, Naime & Yılmaz, & Kara, Murat & Özçakar, Levent. (2017). Effects of Pilates and yoga in patients with chronic neck pain: A sonographic study. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 50. 10.2340/16501977-2288. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321176195_Effects_of_Pilates_and_yoga_in_patients_with_chronic_neck_pain_A_sonographic_study
- E, Nandita & Dowle, Praveen & KS, Asif. (2018). Effectiveness of Pilates as an Adjunct to Conventional Therapy in Chronic Mechanical Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Novel Physiotherapies. 08. 10.4172/2165-7025.1000381. https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/effectiveness-of-pilates-as-an-adjunct-to-conventional-therapy-in-chronic-mechanical-neck-pain-a-randomized-controlled-trial-2165-7025-1000381-99234.html



