The superior Moringa nutritional content makes its products one of the most nutrient‐rich plants on earth11.
Due to its power-packed nutritional profile, Moringa will increase your energy levels fighting fatigue, and provide you with significant support to recover faster after your long hours at work, exercise, and sport.
This awesome superfood provides your body with strong anti-inflammatory proprieties, and a full amino acids profile therefore, it is a complete protein.
But, Moringa’s benefits and uses extends beyond your athletic recovery.
Moringa will prevent malnutrition and fill nutritional gaps adding further benefits to patients with cancer and diabetes type 2.
This plant’s nutritional applications are endless.
Moringa is undoubtedly the champion of greens!
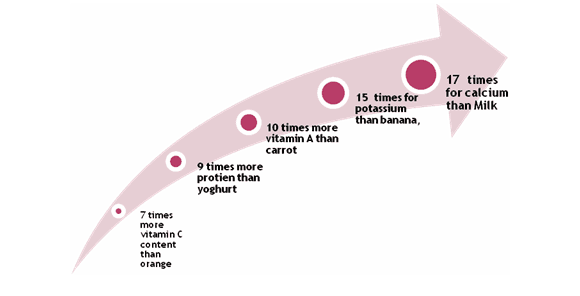
Every 100 grams of Moringa Oreifela leaf powder contains:
- 9 × Protein than yogurt.
- 10 × Vitamin A than carrots.
- 15 × Potassium than bananas.
- 17 × Calcium than milk.
- 7 × Vitamin C than oranges.
• 25 X Iron than Spinach12
Moringa is also a wholesome protein
Ask an athlete or a gym-expert what protein supplement means to them?
Although it is overrated in a simple statement, protein is the building blocks of your body.
The growth, food metabolism, and body tissue repairing are just some of the important functions of the protein.
Amino acids are organic compounds, which jointly forms protein13 by linking with each other through a peptide bond and forms protein structure.
Peptide bonds are a special type of covalent bond which joins two amino acids14.
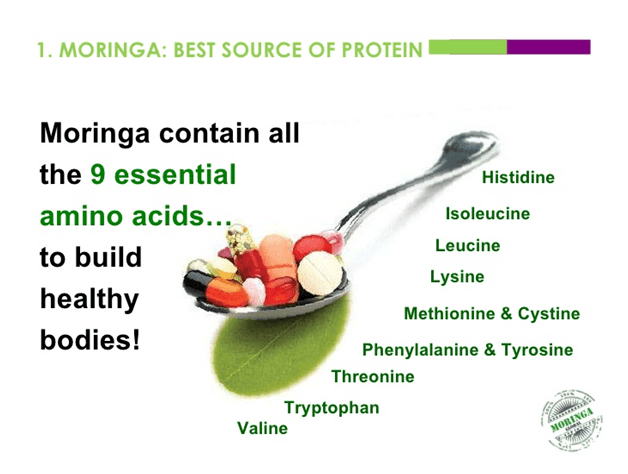
There are nine essential amino acids which cannot be produced in the body and food is the only source for these amino acids13.
Each of these nine essential amino acids has their own function and the deficiency leads to different ailments.
The protein content in Moringa makes this plant a wholesome protein source.
Surprisingly (again), Moringa possess all these nine essential amino acids all together in its nutritional structure.
Here is the list of the nine essential amino acids containing their functioning and deficiency effects:
- Valine: This essential amino acid has a stimulant property and helps to maintain energy level and enhance endurance.
It is essential for muscle growth and tissue repair 15.
Valine deficiency causes significant neurological defects in the brain 16.
- Lysine: This essential amino acid regulates the functioning of the mammary gland, pineal gland, and ovaries.
Lysine has an anti-ageing property and plays multiple functions such as:
- Bone and muscle development,
- Growth by improving calcium absorption,
- Helps in antibodies,
- Collagen,
- Hormone production,
- Build muscle tissue.
Lysine deficiency causes:
- Anaemia,
- Fatigue,
- Depression,
- Infertility,
- Lack of concentration,
- Growth retardation,
- Muscle loss,
- Hair loss, and
- Irritability 17.
- Leucine:
This essential amino acid plays multiple physiological functioning in our body like:
- Protein synthesis,
- Reduce break down of protein,
- Stimulates insulin release and
- Maintains muscle health 18.
Leucine :
- Reduced feeding due to loss of appetite,
- Weight loss,
- Lethargy,
- Poor growth,
- Desquamation,
- Skin rashes, and hair loss 19.
4. Histidine: In our physiological system this amino acid alters in different forms and plays multiple roles.
Histamine, glutamate, and hemoglobin are the converted forms of histidine.
Do you know that each of these have special physiological roles in our body?
Histamine regulates local immune functioning of the body, glutamate is an important neurotransmitter and hemoglobin is an important red blood cell component 20, 21, 22.
- It helps in iron formation by producing ferritin23.
Histidine also helps to:
- Detoxifies the body from heavy metals,
- Regulates blood pH,
- Reduces allergy symptom,
- Boosts the immune system, for myelin sheath on nerve tissue23.
Histidine deficiency leads to:
- Skin and mucous membrane inflammatory condition,
- Aggravate allergic reactions
- Increase infection susceptibility 23.
5. Isoleucine: This essential amino acid helps in muscle recovery, regularises blood sugar levels and maintains energy levels by utilising glucose.
Deficiency of isoleucine can be significantly noticed by muscle tremors 24.
6. Methionine:
This amino acid regulates metabolic processes, the inherent immune system functioning, and digestive functioning.
It also activates antioxidant functioning and prevents oxidative stress 25.
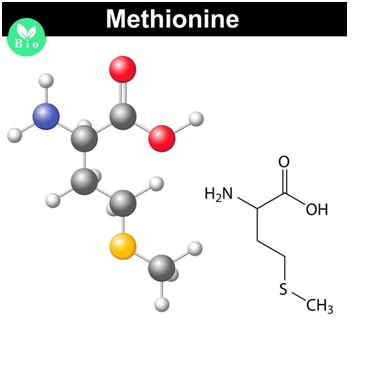
Methionine deficiency causes:
- Reduced growth performance,
- Mitochondrial defect, and
- Reduced oxidative status in liver 26.
7. Threonine:
This is an amino acid, which helps to regulate protein balance in the body.
Threonine provides digestive tract protection by producing mucus gel covering.
Thymus gland uses threonine to produce T-cells and thus boost immune system functioning.
The collagen and elastin needs threonine to build their protein structure and fight against depression.
Threonine deficiency leads to:
- Digestion problems,
- Fatty liver,
- Confusion and
- Mental agitation, etc 27.
8. Phenylalanine:
The metabolic product of phenylalanine amino acid helps to synthesise neurotransmitters and hormones.
This study show that a major deficiency of phenylalanine could be one of the cause of depression 28.
9. Tryptophan:
This amino acid helps in new protein formation in the body.
It also regulates appetite and sleep cycle.
Tryptophan deficiency causes neuropsychological imbalance due to the reduction of serotonin levels, which include:
- anxiety,
- depression,
- insomnia,
- carbohydrate cravings, and
- obesity 29.
Moringa benefits in sport are simply unsurpassed.
Therefore, the question I would like to ask you now is are you supporting your health and sport recovery with Moringa?
If you are planning to do this, ideally you should look for organic and raw moringa.
Pregnancy
Here I have a word of caution…
If you are pregnant or trying to conceive please do not use or incorporate moringa into your list of supplements since, it has antifertility and abortifacient properties.
The next article about Moringa applications will show you the latest research involving Moringa in:
- bronchitis;
- skin disorders and eczema;
- blood pressure;
- cardiovascular disease;
- stroke;
- prostate cancer;
- inflammation and different types of cancer growth;
- anaemia; and
- brain performance.
Come back for more and stay tuned.
You can also contact us on 020 3633 2299.
References
- Oluwole S. Ijarotimi, Oluwole A. Adeoti, Oluwaseun Ariyo. Comparative study on nutrient composition, phytochemical, and functional characteristics of raw, germinated, and fermented Moringa oleifera seed flour. Food Science and Nutrition. Volume1, Issue6. November 2013. Pages 452-463. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.70. Online available at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/fsn3.70
- Lakshmipriya, Gopalakrishnan, KruthiDoriya, Devarai, Santhosh Kumar. Moringa oleifera: A review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application. Food Science and Human Wellness. Volume 5, Issue 2, June 2016, Pages 49-56. Online available athttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213453016300362
- Amino acids. MedlinePlus. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Online available athttps://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002222.htm
- Peptide bond. Biology Dictionary. https://biologydictionary.net/peptide-bond/
- PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Online available athttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Valine#section=Pharmacology-and-Biochemistry
- L-Valine. The Metabolomics Innovation Centre. Online available athttp://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000883
- World Health.Net Online available athttps://www.worldhealth.net/news/lysine/
- D- Leucine. PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Online available athttps://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/d-leucine
- Rebecca S. Wappner, K. Michael Gibson. Disorders of Leucine Metabolism. Online available athttp://eknygos.lsmuni.lt/springer/365/59-79.pdf
- Anna CláudiaCalvielli Castelo Branco, FábioSeiti Yamada Yoshikawa, Anna Julia Pietrobon, Maria Notomi Sato. Role of Histamine in Modulating the Immune Response and Inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2018; 2018: 9524075. Published online 2018 Aug 27. doi: 10.1155/2018/9524075. Online available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6129797/
- Zhou, N. C. Danbolt. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the healthy brain.
J Neural Transm. 2014; 121(8): 799–817. Published online 2014 Mar 1. doi: 10.1007/s00702-014-1180-8. Online available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4133642/ - Blood Basics. American Society of Hematology. https://www.hematology.org/Patients/Basics/
- aminoacidstudies.org. Online available at https://aminoacidstudies.org/l-histidine/
- aminoacidstudies.org. Online available at https://aminoacidstudies.org/l-isoleucine/
- Martínez Y, Li X, Liu G, Bin P, Yan W, Más D, Valdivié M, Hu CA, Ren W, Yin Y. The role of methionine on metabolism, oxidative stress, and diseases. Amino Acids.2017 Dec;49(12):2091-2098. doi: 10.1007/s00726-017-2494-2. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Online available athttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28929442
- Sarah Séité, Arnaud Mourier, Nadine Camougrand, Bénédicte Salin, Cláudia Figueiredo-Silva, Stéphanie Fontagné-Dicharry, Stéphane Panserat, Iban Seiliez. Dietary methionine deficiency affects oxidative status, mitochondrial integrity and mitophagy in the liver of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Scientific Reports 8, Article number: 10151 (2018). Online available athttps://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-28559-8
- aminoacidstudies.org. Online available athttps://aminoacidstudies.org/l-threonine/
- ScienceDirect. Online available at https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/phenylalanine
- Online available athttps://restorativemedicine.org/library/monographs/tryptophan/



