The term ‘super’ is used to declare superiority, may it be Superman or Superfood.
It symbolizes enormous power and ability to solve problems.
Similarly, superfood gives the power to fight against diseases and aging due to its great nutritional composition whilst having a low caloric content.
Recently, Moringa proved its ability to be the new superfood, packed with trace minerals and all essential amino acids with the highest protein content of any non-legume plant.
It is an amazing gift of nature, easy to cultivate and accessible to people.
Some interesting facts about Moringa
In recent times, Moringa has pioneered in defining Superfood.
But in traditional history, Moringa was one of the most primitive, and economic crops that grow in the Himalayan foothills.
Extensive cultivation of Moringa occurs across the tropical regions1.
Cultivation and native place of Moringa
The sub-Himalayan region is the native place of Moringa.
A vast area of Africa, Middle East, Asia, America, Cambodia, Philippines, and the Caribbean islands cultivate Moringa.
The documented historical evidence from the early era of the first century A.D. proved that cultivation of Moringa started in India before thousands of years2.
Moringa can withstand drought, and can also be grown in sandy soil which made it a super survival crop.
It has got several names such as:
- Drumstick tree (because of drumstick looking green pods),
- Miracle tree (one solution for many),
- Benzoil tree (because of its oil), and
- Horseradish tree (as the root resembles)3,4.
Moringa in the Royal dish
Believe it or not!
Moringa use to be the secret ingredient in royal dishes, offered to the queen to bestow beauty and ageless skin, and to the king to enhance mental alertness.

Searching ancient history reveals that Indian Maurian warriors used to believe that drinking Moringa elixir prepared from the leaf extract, – helps them to provide:
- Extra energy
- Analgesic effects
- Anti-stress benefits.
Therefore, they used to consume Moringa Leaf Extracts before and during battles.
May this be the surreptitious truth behind their win against the ‘Great Alexander’2?
And if you too, want to win your gym battles J and recover fast after long hours of office work.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!
You can use this delicious energy/sport recovery Moringa smoothie I created for you below here:
- 1 ½ cup of fresh coconut water
- ½ – 1 cup of fresh pineapple
- 1-2 cup of fresh mixed berries (raspberries, strawberries, blueberries)
- 2 large table spoons of organic Moringa powder
- 1 cup of spinach
- 1 table spoon of grinded chia seeds
- 1 heaped tablespoon of plant based protein
Just ensure you don’t have any sensitivities or allergies regarding the ingredients used in the Moringa smoothie recipe.
Why Moringa was introduced as Superfood in Western countries?
Research shows that people in the UK consume high levels of cholesterol rich saturated fat, sugar, and salt-rich food items.
Most of these products are calorie rich but very deficient in essential nutrients.
Research show that in the UK people also eat less:
- Fresh fruits
- Vegetables,
- Fiber-rich foods
- Omega-3 fatty acid5.
And whilst a calorie rich meal makes it easy if you want to gain weight, the lack of nutrients in these foods are increasing iron, calcium, magnesium and other essential nutrients deficiencies.
According to British Nutrition Foundation, mineral intake is low in the UK population, and puts at risk the overall nutritional status of UK population6.
The addition of Moringa-the Superfood, in our daily diet, can supply all the essential nutrients which we commonly lack due to one reason or another.
Therefore the miracle Moringa tree can help you address some of the most complex nutritional deficiencies.
Nothing to discard in Moringa
Moringa is one of the few plants with a variety of nutritional compositions.
The entire plant part possesses potential therapeutic value.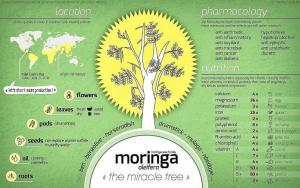
If you grow Moringa plant in your garden, then you can enjoy its multiple therapeutic benefits by not only consuming Moringa leaves, but also the:
- Seeds,
- Flowers,
- Pods,
- Barks, and
- Roots2.
As you can see below all parts of Moringa have different therapeutic benefits.
Moringa – the ultimate nutritional powerhouse fights cholesterol builds up
To improve our health we aim to add multiple fruits and vegetables in our daily diet to get proper nutrition.
Often we take orange to get vitamin C, carrot for vitamin A, banana for potassium, spinach for iron.
Milk and milk products are the major sources of calcium and we consider yogurt for being rich in protein.
However, Some of the countries with the highest osteoporosis rate in the world are the biggest consumers of dairy products7, 8.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!
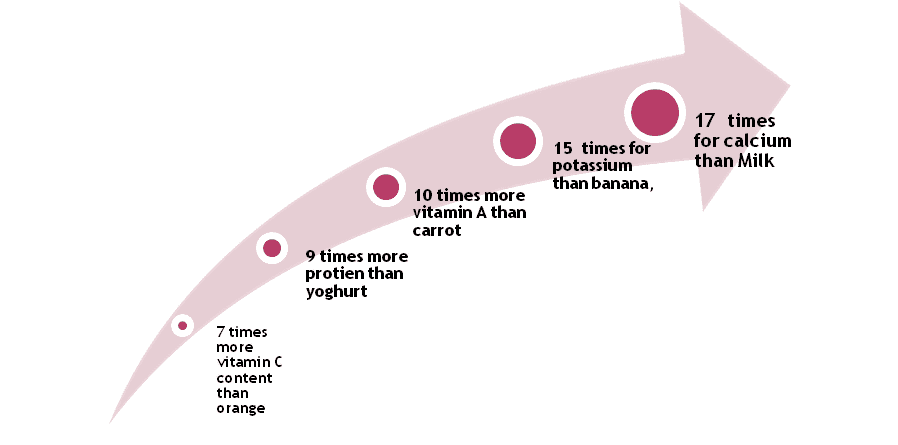
But surprisingly, Moringa alone can be the best alternative for these multiple food items.
The dark green Moringa supplies 25 times more iron than spinach9.
Let me explain this through an info-graphic which will surely impact on your outlook on Moringa.
We all know about the powers of high density lipoprotein (HDL), which is considered as good cholesterol.
HLD helps to remove some of the bad cholesterols such as low density lipoprotein (LDL).
Moringa leaf helps to improve the HDL level in our blood and prevents the dyslipidemic condition10, 11, and 12.
Not only have these, but the high content of all the essential macro and micro ingredients also made Moringa as a God gifted tree or a miracle tree.
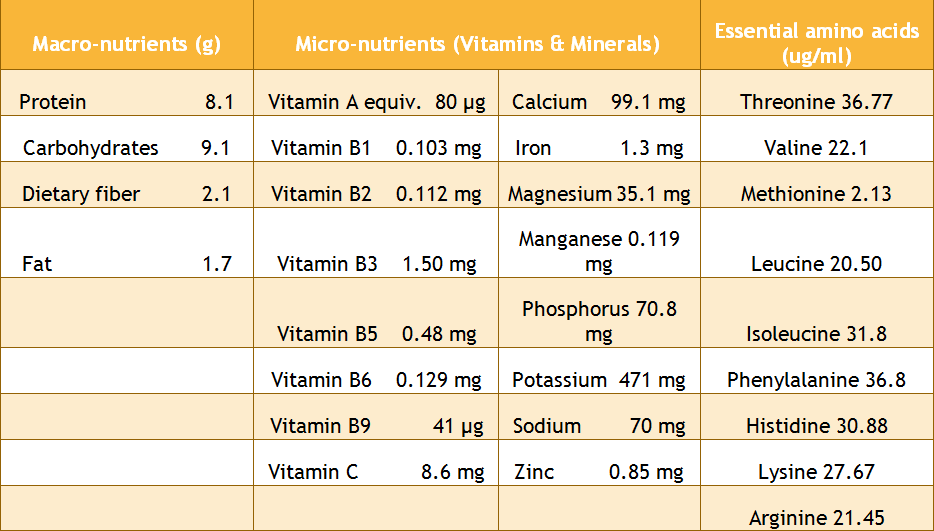
Recently, a detailed nutritional analysis has been conducted, which I am just sharing with you in the below-mentioned table13.
This proves why when Moringa is in your daily diet it helps you to close your nutritional gaps and compensate for all the required nutrition.
 Here are more scientifically proven health benefits of Moringa
Here are more scientifically proven health benefits of Moringa
Provides proper nourishment to body
Adding Moringa in your daily diet can improve your life through nutritional quality by supplying some essential nutrients including trace mineral like:
- Copper,
- Iron,
- Manganese, and
- Zinc along with the adequate amount of
- Protein and
- Vitamin A.
In 2017, a small scale randomized clinical trial showed that M. oleifera leaf fortified foods could adequately supply all the essential nutrients14.
Last year, another pilot study reported M. oleifera leaf fortified foods can prevent vitamin A deficiency diseases by supplying an adequate amount of β‐carotene and other minerals15.
These evidential reports support the efficacy of Moringa in body nourishment.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!
Reduces inflammation
Inflammation is one of the major underlying causes of many chronic diseases.
In our day to day life, stress and other factors increase the burden of free oxygen radicals (ROS) in our body system and among other contributing factors lead to inflammatory conditions like:
- IBD,
- Arthritis,
- Asthma and
- Edema.
Here is how inflammation can affect your body.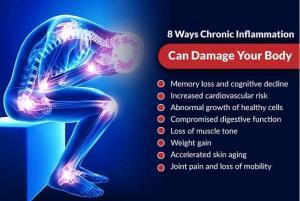
Moringa contains 46 antioxidants and 36 anti-inflammatory phytochemicals.
The anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects of Moringa provide an alternative treatment for inflammatory bowel diseases (IBS)16.
Certain anti-inflammatory phytochemicals like Beta-sitosterol, caffeoylquinic acid and isothiocyanates present in Moringa impart anti-inflammatory property17,18.
The Moringa (MO) root extract is beneficial for arthritis, as Aurantiamide acetate a rare dipeptide and 1,3-dibenzyl Urea, a rare urea derivative isolated from this plant part.
Both of these phytochemicals have anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects19, because they have inhibitory effect on inflammatory cytokines, such as TNFα and IL-2.
Thus Moringa root extract has antiarthritic activity19, 20.
The potent anti-inflammatory effect of Moringa is effective to reduce asthma and to some extent it helps treating bronchial inflammation21, 22.
A research also showed that Moringa is effective to reduce edema.
The effect is noticeable within 1-hour since the treatment start23.
Improves digestion
Moringa containing very important alkaloids.
These are nitrogen base chemical compounds such as:
- N,α-l-rhamnopyranosyl vincosamide, phenylacetonitrile pyrrolemarumine,
- 4′-hydroxyphenylethanamide-α-l-rhamnopyranoside and its
- Glucopyranosyl derivative24, and
- Other phytochemicals help to reduce gastrointestinal disorders by providing protection against ulcer25.
Moringa has the ability to increase the 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) level by increasing enterochromaffin cells (EC) number in gastrointestinal tract26.
5-HT is alternatively known as Serotoni, a neurotransmitter synthesized in EC present in intestinal mucosa.
Moringa improves the functioning of both 5-HT and EC.
Moringa can also help to improve digestion and absorption by improving neurological coordination and gastric motility27.
The outcome of these physiological benefits helps to prevent:
- Constipation,
- Irritable bowel syndrome,
- Post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome and
- Inflammatory bowel disease27.
Researchers also acknowledged that synthetic antacids (medicine which neutralises excess stomach acid) and antihistamines (medicine blocks the histamine), a neurotransmitter functioning and control the acid secretion from stomach to prevent gastric irritation29 could replace by alternative herbal treatment of Moringa.
Even preventive treatment of Moringa is effective to reduce the scope of gastro-intestinal surgery26.
The vitamin B content present in Moringa helps in:
- Food digestion,
- Utilisation of food energy and
- Preventing deposits of fat storage30.
The liver protective effect and anti-diarrheal properties of Moringa improve:
- Digestion and
- Prevent common stomach problems31.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!
Enables muscle growth
The protein present in Moringa can preserve physiological functioning, and build different body tissues including cellular structure, bones, and muscles.
Protein is also essential for muscle repair and building etc.
Just one intake of 100 g Moringa leaf alone can supply 8.1 g protein13.
Protein is made up of a sequence of amino acids.
We need almost 20 amino acids to prepare necessary proteinaceous structures of our body.
Among them, our body itself can prepare almost 11 amino acids, but the remaining nine essential amino acids must be obtained from a proper diet.
Surprisingly, Moringa alone contains all these nine essential amino acids.
Therefore, the addition of Moringa in the diet can never create a deficiency of essential amino acids31.
Boosts immunity
Moringa has potent antioxidant effect with an abundant source of:
- Vitamin A,
- Vitamin C,
- Vitamin E.
The natural combination of these vitamins improves your:
- Immunity and
- Reduce the risk of disease.
A human study conducted in 1991 reported combinations of vitamin A, C, and E supplement for 28 days therapy improves immune parameters among the elderly due to their potent antioxidant activity32.
Lysine amino acid present in Moringa can produce natural antibodies and strengthen our immune system13, as Lysine is present in leukocytes and in protective proteins, which are essential for immune response33.
Fights bacterial diseases
Research shows that moringa oleifera (MO) has very strong antimicrobial property31.
Traditionally, MO used to treat common cold, fever, and improve sexually transmitted infections like syphilis.
- Moringa is effective to a large extent against both fungal and viral infections including herpes and HIV34.
- aureus, V. cholerae, and E. coli are the bacteria susceptible to Moringa35.
- 4-(a-L-rhamnopyranosyloxy) benzyl glucosinolates and its cognate isothiocyanate, present in the MO have a wide range of anti-microbial effect.
- pylori are one of the common bacteria affect human gastric cells and causes a gastric ulcer.
According to the pilot study, H.pylori has sensitivity against isothiocyanate34.
Weight management
You can clearly say that whilst Moringa can help you maintain your muscles mass due the excellent protein content13 it also helps you to achieve muscle definition and kill two birds with one stone etc.
The presence of all these important essential nutrients makes Moringa leaves an ideal dietary supplement.
Moringa is a great filler and acts as a natural appetite suppressant.
This property of hunger suppression makes Moringa most powerful slimming agents, increasing metabolism.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!
The abundant source of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients provides a perfect balanced diet through triggering natural energy production without resulting in any dangerous side effects like other slimming pills and slimming agents36.
Moringa is a slimming agent but significantly helps to improve your energy level.
Healthier bones
Reduction of bone density with increasing age is a major common problem.
Especially, women face such issues after menopause.
Supplying essential nutrients to an adequate level can help to prevent continuous bone loss deterioration.
Moringa is packed with bone-healthy nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and phosphorus helps to keep the bone density intact.
A randomised placebo-controlled human trial was conducted in 2015 to evaluate the bone-health benefits of Moringa with 1000 mg dose37.
Moringa is very useful to prevent osteoporosis.
Moringa fruits and flower have a positive effect on osteoblastic cells and help in bone tissue formation, increase collagen and bone mineral content.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!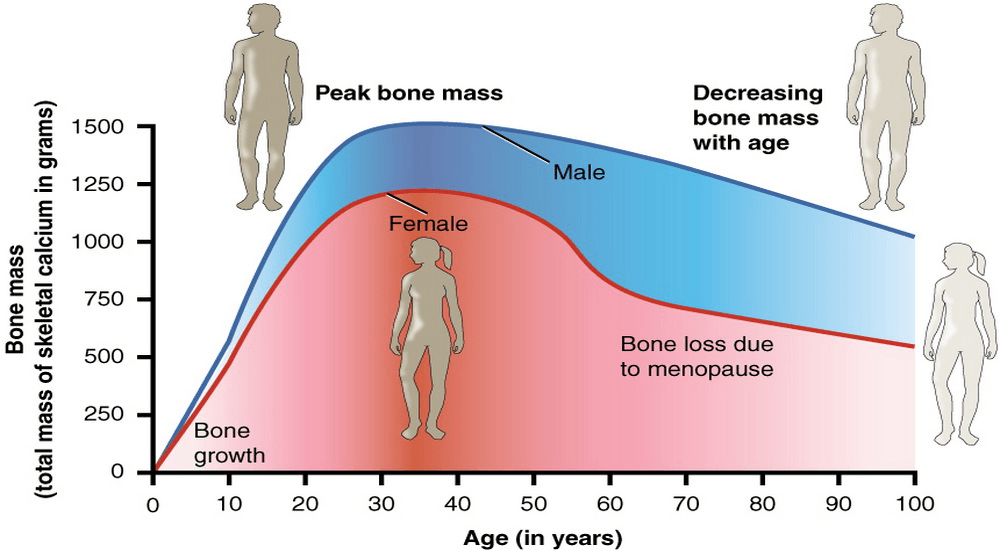
Therefore, Moringa supplementation helps to maintain and improve healthy bone structure to any age group38.
Improves vision
Nowadays, poor vision is not an age-related problem!
Even kids are seen using a thick pair of glasses.
One of the major cause of poor eye-sight is a deficiency of vitamin A.
Fast foods, ready meals food habits and sedentary lifestyle can change our taste buds.
We also eat less leafy vegetables and colorful fruits, which makes our vitamin A intake to dramatically drop.
Moringa superfood is a solution for this problem due to an abundant source of vitamin A present in its leaves, pods, which prevent poor vision and night blindness.
If you have a higher risk to develop a cataract, then taking Moringa leaf preparation can delay its development39.
Anti-Diabetic
Are you diabetic and searching for some foods or natural therapy to control your blood glucose level?
Moringa herbal supplement is the right alternative choice for you.
- According to the research experts, the combination of polyphenols compounds (rutin, quercetin-3-glycoside, kaempferol) with glycosides in Moringa provides an anti-diabetic effect40.
- A research showed that Moringa could reverse some of the damage of islet cells, from where insulin releases40.
- Moringa helps better utilisation of glucose by skeletal muscle.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!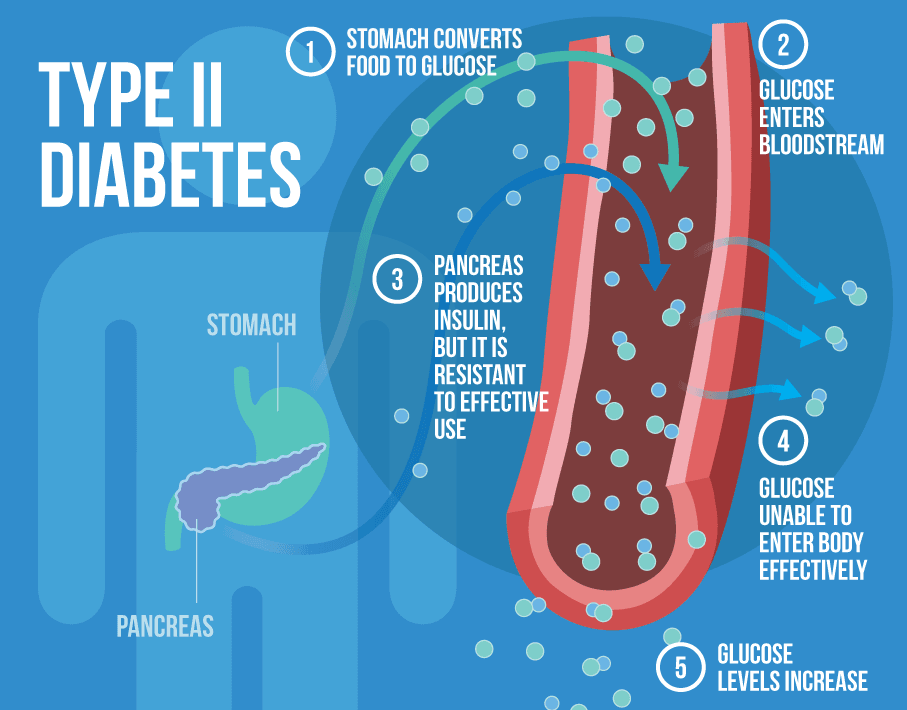
This is possible as Quercetin present in Moringa stimulates glucose transporter proteins (GLUT4) activity in skeletal muscle and thus increases glucose uptake by skeletal muscle40, 41.
It also increases insulin secretion by preventing pancreating cell damage.
- Moringa reduces blood sugar level.
The phenolics and flavonoids phytochemicals present in Moringa helps to reduce oxidative damage in pancreatic tissue and also increases glucose tolerance.
In addition, antidiabetic treatment of Moringa can inhibit alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase enzymes41 and thus delay the metabolism of carbohydrates in the small intestine and reduce the postprandial blood sugar level42.
Helps in lowering cholesterol
Hypercholesteremia or increase in blood cholesterol level is one of the primary cause for cardiovascular disorder43.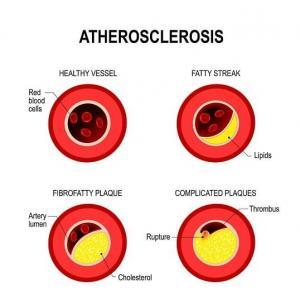
Moringa is a single solution for multiple health issues, including blood cholesterol-lowering benefit.
- Beta-sitosterol, a bioactive constituent present in this herb inhibits the cholesterol synthesis inside the body17.
- Apart from this, the presence of lysine, methionine, and tryptophan amino acids in Moringa enhance lecithin production in the body and helps to lower the blood cholesterol level44.
In a research study, Moringa supplementation had given to the study participants along with a high-fat diet.
The result showed a significant reduction of the high-fat-diet-induced enhancement of cholesterol levels in serum, liver, and kidney45.
Enhances hair and skin health
Beauty is a substantial factor that depends upon the individual’s appearance, but can significantly influence self-confidence.
Few of the cosmetic effects of Moringa as discussed below can enhance and help to persevere your beauty for long.
- Sufficient protein is important to provide nourishment to the skin and rejuvenate the dermatological cells.

Moringa leaves contain all chains of essential amino acids, including:
- Threonine,
- Valine,
- Methionine,
- Leucine,
- Isoleucine,
- Phenylalanine,
- Histidine,
- Lysine and
- Arginine13, which are helpful for skin nourishment as well as for new skin development46.
- Skin vitality is achieved by supplying a sufficient amount of sulfur, the beauty mineral.
Sufficient amount of sulfur in Moringa is a key ingredient of skin collagen and keratin synthesis.
Collagen and Keratin are essential for softness and firmness47.
The abundant supply of anti-oxidants by Moringa supplementation prevents skin aging and the development of wrinkles48.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!
Sufficient amounts of:
- Vitamin A,
- B6,
- Biotin,
- C and
- E
Along with different beneficial minerals like:
- Zinc,
- Iron,
- Calcium,
- Copper,
- Potassium,
- Magnesium,
- Manganese,
- Selenium is helpful to prevent hair fall, split hair, dandruff, and other hair related problems.

Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences published an article in 2014 reported the hair growth activity of Moringa is non-inferior to minoxidil49.
- Moringa, not only prevents the cell damage but promotes the cellular regeneration process.
Zeatin and Healthy Ageing
Zeatin is an active constituent present in Moringa and has premature aging prevention capacity.
Moringa is the only plant source, which supplies an abundant amount of Zeatin.
Sufficient amounts of zeatin enhances skin capacity to resist biochemical alteration that occurs with increasing age and it also prevents skin damage due to UV ray exposure48.
Anti-depressant properties
We expect more from life and sometimes we run behind their desires.
Anxiety and depression is becoming a common mental problem, and life is not always easy.
Sometimes it is hard to deal with increased stress and sometimes it is difficult to deal with life failure.
In many cases like these anti-depressants are routinely described.
But,
Anti-depressant drugs often have many side effects and some people avoid continuing therapy.
However, this study shows that the combination of Moringa with anti-depressant drugs gives better treatment outcomes50.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!
Moringa might lower the daily dose of synthetic medications and treatment duration.
Reduces fatigue
Our day to day work pressure and stress often results in physical and/or mental fatigue and creates a hurdle for continuing daily activities.
There is always a constant search among people for a nutritional supplement which can give a boost to evacuate physical or mental exhaustion.
The consideration of Moringa as a superfood is not a yarn, but it acts as a source of energy to fight against chronic fatigue condition.
An animal research study reported that Moringa leaf supplementation could:
- Delay the lactate and urea nitrogen accumulation in the blood,
- Improve body fat utilization,
- Reduce stored glycogen depletion.
Thus, Moringa helps to maintain energy levels and reduce fatigue51.
Menstruating females often have fatigue compliant due to iron deficiency52.
Dark green colored Moringa is packed with high iron content (1.3 mg iron in 100gm Moringa leaves)13 and can prevent iron deficiencies.
Anti-cancer
Medical developments provided advanced treatment against cancer, but the negative side effects are significant.
Tumour formation is the initial stage of cancer.
Uncontrolled and unwanted malignant cell growth within the tumour, can spread throughout the body like fire.
Moringa, the potent antioxidant source is a natural solution as a chemo-preventive tool thus, it provides some cancer protection benefits.
Progressive free radicals accumulation is one of the primary causes of cancer development and cancer is a multifactorial disease.
Multiple antioxidant-rich phytochemicals like myrecytin, quercetin, kaempferol and Phenolic acids present in Moringa acts against cancer39, 46.
Anti-tumor properties of Moringa leaf extract is a potent inhibitor of lymphoblastoid (Burkitt’s lymphoma) cells and to some extent it prevents cancer development34.
Not only this, animal research studies proved that Moringa enhances glutathione, a potent antioxidant and provides anti-tumor activity22.
Continuous research studies also revealed that Moringa induces apoptosis (the cell death) on ovarian cancer cells, and the ability to inhibit NF-kappaB15.
Another research conducted on Moringa against skin papillomagenesis showed significant reduction of papillomas and tumor multiplicity53.
Aphrodisiac
Aphrodisiac is an agent which has the potential to increase sexual desire.
Due to their stressful life males are often affected by sexual dysfunction.
The leaf of Moringa has an inhibitory effect against 6-β-hydroxylation of testosterone and may enhance sexual potency.
Moringa can decrease stress levels by acting on the dopaminergic neuron.
Moringa leaf improves testosterone synthesis with the enhancement of blood flow54.
Altogether these activities improve:
- Penile erection,
- Regulate sperm maturation and
- Spermatogenesis54.
How to choose the right Moringa for you?
Moringa supplement is already marketed for easy access.
But I will give you some very useful tips, which will help you select right Moringa products.
Select the right species
There are 13 different varieties of Moringa cultivated in a different region of its native places but they are not equal.
Moringa oleifera is the most widely studied species among them.
Most of the above-mentioned health benefits have checked with this species.
Select winter crop
Both summer and winter season are suitable for Moringa cultivation.
But winter crop has a more antioxidant property and the calcium content.
Therefore, ask your vendor to give you winter Moringa products55.
Moringa leaf is best than stem and stalk containing products
- Moringa leaf contains higher antioxidant properties than stem and stalk (leaf > stem > stalk).
- It has studied that methanolic extract of Moringa leaf better for scavenging free radicals as it contains maximum antioxidants-superoxide dismutase proteins in it55.
Combination with Spirulina
Moringa leaf powder with spirulina with 7:3 ratio gives optimum health benefits41.
Spirulina is a type of algae and considered as the most balanced nutritional substance.
High in protein, low fat, and low cholesterol nutrients along with a combination of bioactive compounds like phycocyanin, and γ-linolenic acid, vitamins, minerals and trace elements present in spirulina are very useful for humans.
Combinations of Moringa and spirulina formulation can provide you with a more comprehensive and balanced proportion of nutrients56.
Click here for a FREE CONSULTATION with Jazz today!
References
- The National Academic Press. Lost Crops of Africa: Volume II: Vegetables (2006),Chapter: 14 Moringa, https://www.nap.edu/read/11763/chapter/16#253
- Sujatha B.K & Poonam Patel. Moringa Oleifera – Nature’s Gold. Imperial Journal of Interdisciplinary Research (IJIR) Vol-3, Issue-5, 2017ISSN: 2454-1362, http://www.onlinejournal.in https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317930958_Moringa_Oleifera_-_Nature’s_Gold
- U.M. Ndubuaku, A.E. Ede, K.P. Baiyeri and P.I. Ezeaku, 2015. Application of Poultry Manure and Its Effect on Growth and Performance of Potted Moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam) Plants Raised for Urban Dwellers’ Use. American Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilization Technology, 5: 33-39. DOI: 10.3923/ajpnft.2015.33.39 https://scialert.net/fulltext/?doi=ajpnft.2015.33.39
- Traditional Crops, Moringa. Food and Agriculture Organization of The United Nation. http://www.fao.org/traditional-crops/moringa/en/
- Eating a balanced diet. Eat well. NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/
- Minerals and trace elements. British Nutrition Foundation. https://www.nutrition.org.uk/nutritionscience/nutrients-food-and-ingredients/minerals-and-trace-elements.html?showall=1&limitstart=
- Calcium: What’s Best for Your Bones and Health? The Nutrition Source. Harvard T.H. Chan. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/calcium-and-milk/calcium-full-story/
- Feskanich D, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Frazier AL, Willett WC. Milk consumption during teenage years and risk of hip fractures in older adults. JAMA Pediatr. 2014 Jan;168(1):54-60. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2013.3821. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24247817
- Lakshmipriya Gopalakrishnan, Kruthi Doriya, Devarai Santhosh Kumar. Moringa oleifera: A review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application. Food Science and Human Wellness. Volume 5, Issue 2, June 2016, Pages 49-56. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213453016300362
- Will Hawkins. Health benefits of moringa. PUSH DOCTOR.https://www.pushdoctor.co.uk/blog/health-benefits-of-moringa
- Mehta K, Balaraman R, Amin AH, Bafna PA, Gulati OD. Effect of fruits of Moringa oleifera on the lipid profile of normal and hypercholesterolaemic rabbits. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003 Jun;86(2-3):191-5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12738086
- Manal Mused Almatrafi, Marcela Vergara-Jimenez, Ana Gabriela Murillo, Gregory H. Norris, Christopher N. Blesso, Maria Luz Fernandez. Moringa Leaves Prevent Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation in Guinea Pigs by Reducing the Expression of Genes Involved in Lipid Metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul; 18(7): 1330. Published online 2017 Jun 22. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071330. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5535825/
- Abbas et al., Nutritional Values of Moringa oleifera, Total Protein, Amino Acid, Vitamins, Minerals, Carbohydrates, Total Fat and Crude Fiber, under the Semi-Arid Conditions of Sudan. J MicrobBiochemTechnol 2018, 10:2 DOI: 10.4172/1948-5948.1000396 https://www.longdom.org/open-access/nutritional-values-of-moringa-oleifera-total-protein-amino-acid-vitaminsminerals-carbohydrates-total-fat-and-crude-fiber-under-the-1948-5948-1000396.pdf
- Mary Glover‐Amengor, Richmond Aryeetey, Edwin Afari, Alexander Nyarko. Micronutrient composition and acceptability of Moringa oleifera leaf‐fortified dishes by children in Ada‐East district, Ghana. Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Mar; 5(2): 317–323. Published online 2016 Jul 5. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.395. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5332270/
- Laurene Boateng, Irene Ashley, Agartha Ohemeng, Matilda Asante, Matilda Steiner-Asiedu. Improving Blood Retinol Concentrations with Complementary Foods Fortified with Moringa oleifera Leaf Powder – A Pilot Study. Yale J Biol Med. 2018 Jun; 91(2): 83–94. Published online 2018 Jun 28. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6020727/
- Mohsen Minaiyan, Gholamreza Asghari, Diana Taheri, Mozhgan Saeidi, Salar Nasr-Esfahani. Anti-inflammatory effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds on acetic acid-induced acute colitis in rats. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2014 Mar-Apr; 4(2): 127–136. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4103706/
- Ty Bollinger. Moringa oleifera – Miracle tree. Cancer Tutor. https://www.cancertutor.com/moringa-oleifera/
- Carrie Waterman, Diana M. Cheng, Patricio Rojas-Silva, Alexander Poulev, Julia Dreifus, Mary Ann Lila, Ilya Raskin. Stable, water extractable isothiocyanates from Moringa oleifera leaves attenuate inflammation in vitro. Phytochemistry. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 Jul 1. Published in final edited form as: Phytochemistry. 2014 Jul; 103: 114–122. Published online 2014 Apr 11. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.03.028. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4071966/
- Sashidhara KV, Rosaiah JN, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Raghubir R, Rajendran SM. Rare dipeptide and urea derivatives from roots of Moringa oleifera as potential anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2009 Jan;44(1):432-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2007.12.018. Epub 2007 Dec 28. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18243423
- Sashidhara KV, Rosaiah JN, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Raghubir R, Rajendran SM. Rare dipeptide and urea derivatives from roots of Moringa oleifera as potential anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2009 Jan;44(1):432-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2007.12.018. Epub 2007 Dec 28. https://www.academia.edu/16629131/Rare_dipeptide_and_urea_derivatives_from_roots_ of_Moringa_oleifera_as_potential_anti-inflammatory_and_antinociceptive_agents_
- Michael Ravensthorpe. Moringa oleifera is a potent anti-inflammatory, study finds. 2013. https://www.naturalnews.com/043310_Moringa_oleifera_anti-inflammatory_herbal_medicine.html
- Moringa oleifera. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/integrative-medicine/herbs/moringa-oleifera
- Ndiaye M, Dieye AM, Mariko F, Tall A, Sall Diallo A, Faye B. [Contribution to the study of the anti-inflammatory activity of Moringa oleifera (moringaceae)]. Dakar Med. 2002;47(2):210-2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15776678
- Marcela Vergara-Jimenez, Manal Mused Almatrafi, Maria Luz Fernandez. Bioactive Components in Moringa Oleifera Leaves Protect against Chronic Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2017 Dec; 6(4): 91. Published online 2017 Nov 16. doi: 10.3390/antiox6040091. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5745501/
- Debnath S, Biswas D, Ray K, Guha D. Moringa oleifera induced potentiation of serotonin release by 5-HT(3) receptors in experimental ulcer model. Phytomedicine. 2011 Jan 15;18(2-3):91-5. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2010.06.003. Epub 2010 Jul 16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20637582
- Debnath S, Guha D. Role of Moringa oleifera on enterochromaffin cell count and serotonin content of experimental ulcer model. Indian J Exp Biol. 2007 Aug;45(8):726-31. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17877150
- Costedio MM, Hyman N, Mawe GM. Serotonin and its role in colonic function and in gastrointestinal disorders. Dis Colon Rectum. 2007 Mar;50(3):376-88. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17195902
- The Functions of Histamine. http://sepa.duq.edu/regmed/immune/histamine.html
- Lora V. Hooper. Epithelial Cell Contributions to Intestinal Immunity. Advances in Immunology, 2015. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/enteroendocrine-cell
- Meenakshi Nagdeve. 18 Science-Based Benefits & Uses Of Moringa Oleifera. May 12, 2019. https://www.organicfacts.net/health-benefits/vegetable/moringa.html
- Dhakar RC, Maurya SD, Pooniya BK, Bairwa N, Gupta M, Sanwarmal. Moringa : The herbal gold to combat malnutrition. Chron Young Sci [serial online] 2011 [cited 2019 May 23];2:119-25. Available from: http://www.cysonline.org/text.asp?2011/2/3/119/90887. http://www.cysonline.org/article.asp?issn=2229-5186;year=2011;volume=2;issue=3;spage=119;epage=125;aulast=Dhakar;type=3
- Penn, N.D., L. Purkins, J. Kelleher, R.V. Heatley, B.H. Mascie-Taylor, and P.W. Belfield. 1991. The effect of dietary supplementation with vitamins A, C and E on cell-mediated immune function in elderly long-stay patients: A randomized controlled trial. Age Ageing 20:169-174 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1853789
- V. J. Iseri, K. C. Klasing, Changes in the Amount of Lysine in Protective Proteins and Immune Cells after a Systemic Response to Dead Escherichia coli: Implications for the Nutritional Costs of Immunity, Integrative and Comparative Biology, Volume 54, Issue 5, November 2014, Pages 922–930, https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/icu111. https://academic.oup.com/icb/article/54/5/922/2797878
- Jed W. Fahey. Moringa oleifera: A Review of the Medical Evidence for Its Nutritional, Therapeutic, and Prophylactic Properties. Part 1. Trees for Life journal. December 1, 2005. https://www.tfljournal.org/article.php/20051201124931586
- Gustavo Hitzschky Fernandes VIEIRA, Jozeanne Alves MOURÃO, Ângela Maria ÂNGELO, Renata Albuquerque COSTA, Regine Helena Silva dos Fernandes VIEIRA. ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT (in vitro) OF Moringa oleifera AND Annona muricata AGAINST GRAM POSITIVE AND GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 52(3):129-132, May-June, 2010 doi: 10.1590/S0036-46652010000300003. http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rimtsp/v52n3/a03v52n3.pdf
- Moringa – Most Nutritious Plant On Land (Summary). Research on Moringa. http://researchonmoringa.blogspot.com/
- Effect of Moringa Oleifera on Bone Density in Post-Menopausal Women. Moringa Oleifera on Bone Density. https://ichgcp.net/clinical-trials-registry/NCT03026660
- Chirag Patel, Ayaz Rangrez, Pragna Parikh. The anti-osteoporotic effect of Moringa oliefera on osteoblastic cells: SaOS 2. IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-ISSN: 2278-3008. Volume 5, Issue 2 (Jan. – Feb. 2013), PP 10-17. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235952240_The_anti-osteoporotic_effect_of_Moringa_oliefera_on_osteoblastic_cells_SaOS_2
- Marcela Vergara-Jimenez, Manal Mused Almatrafi, Maria Luz Fernandez. Bioactive Components in Moringa Oleifera Leaves Protect against Chronic Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2017 Dec; 6(4): 91. Published online 2017 Nov 16. doi: 10.3390/antiox6040091. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5745501/
- Villarruel-López, D. A. López-de la Mora, O. D. Vázquez-Paulino, A. G. Puebla-Mora, Ma R. Torres-Vitela, L. A. Guerrero-Quiroz, K. Nuño. Effect of Moringa oleifera consumption on diabetic rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018; 18: 127. Published online 2018 Apr 10. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2180-2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5894151/
- Washim Khan, Rabea Parveen, Karishma Chester, Shabana Parveen, Sayeed Ahmad. Hypoglycemic Potential of Aqueous Extract of Moringa oleifera Leaf and In Vivo GC-MS Metabolomics. Front Pharmacol. 2017; 8: 577. Published online 2017 Sep 12. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00577. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5601078/
- M. I. Kazeem,1 J. O. Adamson,1 and I. A. Ogunwande2. Modes of Inhibition of α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase by Aqueous Extract of Morinda lucida Benth Leaf. BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 527570, 6 pages. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/527570. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2013/527570/
- Leer en español. High Blood Cholesterol. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/high-blood-cholesterol
- Drew Canole. 13 Moringa Oleifera Benefits Backed By Science. 2014. http://fitlife.tv/the-green-herb-that-flushes-toxins-and-fights-cancer-with-no-known-side-effects/uncategorized/
- S. Ghasi, E N wobodo, J. O Ofili. Hypocholesterolemic effects of crude extract of leaf of Moringa oleifera Lam in high-fat diet fed wistar rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. Volume 69, Issue 1, January 2000, Pages 21-25. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378874199001063
- Michael Ravensthorpe. The many health benefits of Moringa oleifera. Natural News. 2013. https://www.naturalnews.com/042435_Moringa_oleifera_health_benefits_herbal_medicine.html
- Moringa Nutrient For Skin. Research on Moringa. http://researchonmoringa.blogspot.com/2012/09/moringa-nutrient-for-skin.html
- Moringa and Anti-Ageing. https://www.moringaharvest.co.uk/pages/anti-ageing
- Philip F. Builders et. al. Moringa OleiferaEthosomes a Potential Hair Growth Activator: Effect on Rats. ISSN NO- 2230 – 7885 CODEN JPBSCT NLM Title: J Pharm Biomed Sci. pp- 611 – 618
- Xianjuan Kou, Biao Li, Julia B. Olayanju, Justin M. Drake, Ning Chen. Nutraceutical or Pharmacological Potential of Moringa oleifera Lam. Nutrients. 2018 Mar; 10(3): 343. Published online 2018 Mar 12. doi: 10.3390/nu10030343. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5872761/
- Bonoy Lamou, Germain Sotoing Taiwe, André Hamadou, Abene, Justin Houlray, Mahamat Mey Atour, Paul Vernyuy Tan. Antioxidant and Antifatigue Properties of the Aqueous Extract of Moringa oleifera in Rats Subjected to Forced Swimming Endurance Test. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016: 3517824. Published online 2016 Jan 19. doi: 10.1155/2016/3517824. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4745945/
- Esa T. Soppi. Iron deficiency without anemia – a clinical challenge. Clin Case Rep. 2018 Jun; 6(6): 1082–1086. Published online 2018 Apr 17. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.1529. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5986027/
- Bharali R, Tabassum J, Azad MR. Chemomodulatory effect of Moringa oleifera, Lam, on hepatic carcinogen metabolising enzymes, antioxidant parameters and skin papillomagenesis in mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2003 Apr-Jun;4(2):131-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12875626
- Thawatchai Prabsattroo, Jintanaporn Wattanathorn, Sitthichai Iamsaard, Pichet Somsapt, Opass Sritragool, Wipawee Thukhummee, Supaporn Muchimapura. Moringa oleifera extract enhances sexual performance in stressed rats. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015 Mar; 16(3): 179–190. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1400197. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4357367/
- Ming-Chih Shih, Cheng-Ming Chang, Sue-Ming Kang, Min-Lang Tsai. Effect of Different Parts (Leaf, Stem and Stalk) and Seasons (Summer and Winter) on the Chemical Compositions and Antioxidant Activity of Moringa oleifera. Int J Mol Sci. 2011; 12(9): 6077–6088. Published online 2011 Sep 19. doi: 10.3390/ijms12096077. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3189769/
- Yi Zheng, Fan Zhu, Dan Lin, Jun Wu, Yichao Zhou, Bohn Mark. Optimization of formulation and processing of Moringa oleifera and spirulina complex tablets. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2017 Jan; 24(1): 122–126. Published online 2016 Sep 8. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.08.017. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5198973/




 Here are more scientifically proven health benefits of Moringa
Here are more scientifically proven health benefits of Moringa