Your Body Mass Index is often considered one of the key health markers.
Many doctors will measure your BMI to help them determine the risk of suffering from certain diseases.
When the BMI is higher than 25, it means we are overweight.
Once it reaches 30, we are classified as obese.
There are several medical risks associated with high BMI.
You are at a higher risk of depression, osteoarthritis, diabetes, heart disease, and osteoarthritis when you are obese1.

While a BMI between 20 and 25 is generally considered normal, this does not necessarily mean you have no need to worry about health risks.
Even if your doctor finds that your BMI is within a normal range, you should still ask them to check specific health markers before giving you a clean bill of health.
One to one training and customised nutrition helps getting your BMI to a normal range and significantly reduces your risk of serious chronic diseases.
If weight gain is affecting your health, request a FREE CONSULATION now with Jazz Alessi the elite personal trainer in London.
Important Health Markers To Check If Your BMI Is Normal
Doctors always advise that disease prevention is key.
Once your BMI has been measured and is determined to be normal, your checkup with a physician should not be over.
In addition to checking your BMI, you should ask your doctor to do a couple of additional tests.
We’ll outline some of the most important health markers that you might like to consider testing.
All of these health markers can give you a better view of how healthy you truly are at the moment, and give you access to information needed to identify your own risks of certain chronic conditions.
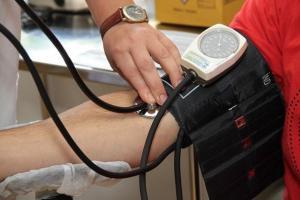
1. Blood Pressure Test
Your blood pressure tells you how hard your heart is working to pump blood through your body.
When your blood pressure is high, you are at risk of blood vessel damage.
You are also at a higher risk of poor blood circulation, a weak heart, heart attacks, kidney damage, and a stroke2.
Blood pressure measurement will give you two different readings.
These include systolic pressure and diastolic pressure.
Normal blood pressure levels should fall in a range from 90/60 mm Hg up to 120/80 mm Hg3.
If your blood pressure is higher than 140/90 mm Hg, then you have high blood pressure.
On the other hand, when your reading is lower than 90/60 mm Hg, then you have low blood pressure.
2. LDL – Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol TesT
Low-Density Lipoprotein cholesterol is usually referred to as LDL cholesterol.
You may hear people refer to this as “poor” cholesterol.
This is the type of cholesterol that raises your risk of certain conditions, including atherosclerosis.
When your LDL cholesterol is high, you are more likely to develop the peripheral arterial disease and coronary artery disease.
Your risk of suffering a stroke also increases as your LDL cholesterol levels rise4.
Normal LDL cholesterol readings should be less than 3 mmol/L.
People who are already at risk of certain conditions associated with high LDL cholesterol should aim for a reading that is less than 2 mmol/L5.
3. Total Cholesterol Test
Total cholesterol is a combined reading that takes both your LDL and HDL cholesterol levels into account.
This reading essentially tells you how good of a balance your cholesterol has – you want your total cholesterol reading to be low, along with your LDL cholesterol reading.
Healthy adults should have a total cholesterol reading that is lower than 5 mmol/L.
If you have been found to be at a high risk of heart disease and related conditions, then your reading for total cholesterol should be below 4 mmol/L.
4. HDL – High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Test
High-Density Lipoprotein cholesterol is usually called good cholesterol.
When you are tested for this particular lipoprotein, the test results will provide the reading as HDL cholesterol.
This is the type of cholesterol that should have a reading on the higher side, as it helps to keep your blood clean and avoids the clogging of LDL cholesterol.
You should aim to maintain an HDL cholesterol reading that is higher than 1 mmol/L.
When your HDL cholesterol falls too low, you may find yourself at a higher risk of cardiovascular disease.
If LDL cholesterol is not in your normal range and it is currently affecting your health, request a FREE CONSULATION now.
Customised nutrition and one to one personal training will help to significantly reduce your risk of serious chronic diseases.
5. ALT – Alanine Aminotransferase Test
Your liver plays several important roles in your body, so getting your ALT levels measured is another important part of ensuring the well-being of your body.
ALT, or alanine aminotransferase, can give a doctor an indication of how effective your liver is functioning.
The measurement for normal ALT levels differ between men and women, as defined below6:
- Men: 29 IU/L to 33 IU/L
- Women: 19 IU/L to 25 IU/L
6. Prostate-Specific Antigen Test
Men should also ensure they get a test for prostate-specific antigen in their body.
This test can provide important data to help the doctor understand how healthy the man’s prostate.
This test can also help to detect possible problems like benign prostatic hyperplasia, as well as prostate cancer.
In many cases, a PSA test will be done on a man who is older than 50 years old.
If you have surpassed this age mark and your PSA levels are higher than 3ng/ml, then this would be considered elevated7.
At this point, your doctor may want to conduct additional tests.
7. Hemoglobin A1c – Diabetes Test
The Hemoglobin A1c test, also called the HbA1c test, is an important way of detecting your risk of diabetes.
This test provides a reading on glycohemoglobin, which gives your doctor a view on your blood sugar levels during the past two to three months.
The HbA1c test provides a percentage as a result.
A normal, healthy person should have a test result that varies from 4% up to 5.6%8.
If your test returns a value between 5.7% and 6.4%, then you are at a higher risk of diabetes.
If your results indicate a value over 6.5%, then you will usually be diagnosed with diabetes.
8. Complete Blood Count Test
A complete blood count can be used as a routine health marker test to determine how healthy your blood is.
This test also provides valuable insight into any potential risks you have for conditions like leukaemia, infections, and anaemia.
Complete blood count provides data on red blood cells, white blood cells, haemoglobin, haematocrit, and platelets.
Each of these readings is provided separately and should be carefully checked to ensure they are within appropriate ranges.
9. Vitamins Levels Test
A screening for vitamins can help you determine if you currently have any nutritional deficiencies related to the most important vitamins your body depends on.
Vitamins are natural substances that perform various functions in the human body.
A deficiency in certain vitamins can greatly increase your risk of developing certain diseases, including a range of chronic illnesses.
10. C-Reactive Protein Test
Another important test you should consider is to detect the level of C-Reactive Protein, or CRP, in your body.
This is an inflammatory marker that can indicate several problems when elevated, including the presence of certain diseases.
A high level of CPR may indicate several potential problems in your body, from simple burns to more serious conditions, like tuberculosis and pneumonia.
Generally, CRP levels should be less than 1 mg per litre of blood.
11. Iron Profile Test
Iron has several important roles to play in your body and helps with the development of blood.
When your iron levels are low, you may be at risk of anaemia and other potential problems.
An iron profile test measures iron levels in your blood and tells you if you might be a risk of an iron deficiency.
12. Thyroid Profile Test
Finally, make sure to have a full thyroid profile test conducted as well.
This test tells your doctor how well your thyroid gland is functioning.
You will usually be tested for both T4 and TSH levels.
When your thyroid hormones are low, then you are at risk of hypothyroidism.
On the other hand, high levels of thyroid hormones may indicate an overactive thyroid gland, also known as hyperthyroidism.
If your health markers are not within the normal range, a personalised exercise programme and nutrition diet plan by an elite personal trainer is a great way to restore your health.
Get in touch with Jazz Alessi today for a FREE CONSULTATION to see how this expert can help you live a healthier life.
Conclusion
Even when your BMI seems to be normal, you could still be at risk of certain conditions.
High body weight is not all that contributes to heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, and other chronic conditions.
Make sure you get your doctor to check for the 12 health markers we outlined here, even when your BMI does seem to be within a normal range.
The National Health Service (NHS) states on its website that as a prevention tool, exercise might reduce early death risks with up to 30 %.
Incredibly, the NHS research also shows that some of the risk of major diseases such as type 2 diabetes, stroke, cancer and heart diseases can also be reduced by up to 50 %.
Whether your BMI is currently a matter contributing to poor health or not, a bespoke diet and exercise plan can help you achieve and maintain a healthy BMI.
At the same time, this type of sharp customised programme gives you the ability to improve the other health markers we looked at significantly.
Get in touch with Jazz Alessi, elite personal trainer, for a FREE CONSULTATION to start your journey to a healthier body.
References
1 X. Pi. Sunyer. The Medical Risks of Obesity. HHS Public Access. 1 Nov 2010. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2879283/
2 High blood pressure: Overview. InformedHealth.org. 21 May 2012. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279239/
3 What is blood pressure? NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/lifestyle/what-is-blood-pressure/
4 T. Huff, I. Jialal. Physiology, Cholesterol. StatPearls. 13 Mar 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470561/
5 Cholesterol. NHS Direct Wales. https://www.nhsdirect.wales.nhs.uk/encyclopaedia/c/article/cholesterol/
6 D. Weatherspoon. ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase) Test. Healthline. 26 Jul 2018. https://www.healthline.com/health/alt#results
7 Should I have a PSA test? NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/prostate-cancer/should-i-have-psa-test/
8 Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test for Diabetes. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/guide/glycated-hemoglobin-test-hba1c